Rennin
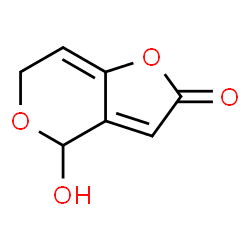
Rennin structure
|
Common Name | Rennin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9001-98-3 | Molecular Weight | 154.120 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 513.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 | Melting Point | 225-227℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 226.8±23.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of RenninRennin, also known as Chymosin, is a pepsin-related proteolytic enzyme synthesized by cells in the stomach of certain animals that efficiently converts liquid milk into a semi-solid, allowing it to remain in the stomach for longer. The natural substrate of Rennin is K-casein, which is specifically cleaved at the peptide bond between amino acid residues 105 and 106, phenylalanine and methionine, and is widely used in cheese production[1]. |
| Name | Rennin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Rennin, also known as Chymosin, is a pepsin-related proteolytic enzyme synthesized by cells in the stomach of certain animals that efficiently converts liquid milk into a semi-solid, allowing it to remain in the stomach for longer. The natural substrate of Rennin is K-casein, which is specifically cleaved at the peptide bond between amino acid residues 105 and 106, phenylalanine and methionine, and is widely used in cheese production[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 513.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 225-227℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 154.120 |
| Flash Point | 226.8±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 154.026611 |
| LogP | -0.75 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.603 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| Hazard Codes | B,Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38-42 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-24-26-36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
|
Proteomic profiling of the coagulation of milk proteins induced by chymosin.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(8) , 2039-45, (2012) Chymosin-induced coagulation of individual milk proteins during incubation at 30 °C was investigated using a proteomic approach. The addition of chymosin (0.006 units/mL) caused the milk proteins to c... |
|
|
Starch addition in renneted milk gels: Partitioning between curd and whey and effect on curd syneresis and gel microstructure
J. Dairy Sci. 95(12) , 6871-81, (2012) Milk gels were made by renneting and acidifying skim milk containing 5 different starches, and then compressed by centrifugation to express whey and simulate curd syneresis during the manufacture of l... |
|
|
Constitutive expression, purification and characterization of bovine prochymosin in Pichia pastoris GS115.
World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28(5) , 2087-93, (2012) Chymosin can specifically break down the Phe105-Met106 peptide bond of milk κ-casein to form insoluble para-κ-casein, resulting in milk coagulation, a process that is used in making cheese. In this st... |
| EINECS 232-645-0 |
| MFCD00132173 |