Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser
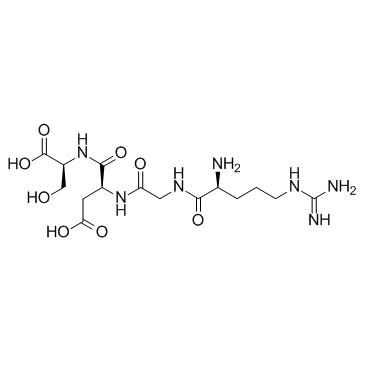
Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser structure
|
Common Name | Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91037-65-9 | Molecular Weight | 433.41700 | |
| Density | 1.65g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H27N7O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Arg-Gly-Asp-SerArg-Gly-Asp-Ser is an integrin binding sequence that inhibits integrin receptor function, decreases systemic inflammation via inhibition of collagen-triggered activation of leukocytes and attenuates expression of inflammatory cytokines, iNOS and MMP-9. |
| Name | RGDS peptide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser is an integrin binding sequence that inhibits integrin receptor function, decreases systemic inflammation via inhibition of collagen-triggered activation of leukocytes and attenuates expression of inflammatory cytokines, iNOS and MMP-9. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | The Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-modified surface causes up-regulation of αvβ3 integrin. Attachment to the Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-treated membrane completely abolishes apoptosis induced by staurosporine, the Ca2+·Pi ion pair, and sodium nitroprusside. Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-dependent resistance to apoptosis is eliminated, when the activity of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway is inhibited[1]. Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser interacts with survivin, as well as with procaspase-3, -8 and -9. Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-peptide binding to survivin is found to be specific, at high affinity (Kd 27.5 μM) and locates at the survivin C-terminus. Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-survivin interaction appears to play a key role, since Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser lost its anti-mitogenic effect in survivin-deprived cells with a specific siRNA[4]. |
| In Vivo | Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (2.5 or 5 mg/kg, 1 h before LPS) significantly inhibits LPS-induced MMP-9 activity in BAL fluid 4 h post-LPS. Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (1, 2.5 or 5 mg/kg, i.p.) administers 1 h before LPS inhibited LPS-induced increases in TNF-α and MIP-2 levels in BAL fluid at 4 h post-LPS[2]. Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser peptide significantly reduces tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-2 production, and decreases myeloperoxidase (MPO) and NF-κB activity[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Cell death is measured using the MTT analysis. This assay is based on the ability of mitochondrial dehydrogenases to oxidize thiazolyl blue (MTT), a tetrazolium salt (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenylterazolium bromide), to an insoluble blue formazan product. The cells are incubated with the MTT reagent (120 μg/mL) at 37°C for 2 h. After the supernatant is removed, 400 μL of 0.04mol/LHCl in isopropanol is added to each well, and the optical density of the solution is read at 590 nm in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay plate reader. As the generation of the blue product is proportional to the dehydrogenase activity, a decrease in the absorbance at 590 nm provides a direct measurement of the number of viable cells. To determine the contribution of the PI3K pathway to inhibition of apoptosis, some cell populations are pretreated with 50 μM LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor. Following this pretreatment, cell death is determined as described above. |
| Animal Admin | Mice pharyngeal aspiration is performed as described. Animals are anesthetized with a mixture of ketamine and xylazine (45 mg/kg and 8 mg/kg, i.p., respectively). Test solution (30 μL) containing LPS (1.5 mg/kg) is placed posterior in the throat and aspirated into the lungs. Control mice are administrated sterile saline (0.9% NaCl). Animals are administered with Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser or RGES peptide (1, 2.5 or 5 mg/kg, i.p.) once one hour before LPS treatment and sacrificed 4 h post-LPS. Animals are also administered Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser or RGES peptide (5 mg/kg, i.p.) once at different time points (1 h before or 2 h after LPS treatment) and sacrificed 24 h post-LPS. In addition, animals are administered with αvβ3-blocking mAbs, anti-αv, or anti-β3 (5 mg/kg, i.p.) once 1 h before and sacrificed 4 h post-LPS. Animals administered with these mAbs 2 h after LPS treatment are sacrificed 24 h post-LPS |
| References |
| Density | 1.65g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H27N7O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 433.41700 |
| Exact Mass | 433.19200 |
| PSA | 270.05000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.659 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Oligodendrocytes Are Targets of HIV-1 Tat: NMDA and AMPA Receptor-Mediated Effects on Survival and Development.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 11384-98, (2015) Myelin pallor in HIV(+) individuals can occur very early during the disease process. While myelin damage might partly originate from HIV-induced vascular changes, the timing suggests that myelin and/o... |
|
|
Emulating native periosteum cell population and subsequent paracrine factor production to promote tissue engineered periosteum-mediated allograft healing.
Biomaterials 52 , 426-40, (2015) Emulating autograft healing within the context of decellularized bone allografts has immediate clinical applications in the treatment of critical-sized bone defects. The periosteum, a thin, osteogenic... |
|
|
Cross-talk between transforming growth factor-β₁ and muscarinic M₂ receptors augments airway smooth muscle proliferation.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 49(1) , 18-27, (2013) Transforming growth factor-β₁ (TGF-β₁) is a central mediator in tissue remodeling processes, including fibrosis and airway smooth muscle (ASM) hyperplasia, as observed in asthma. The mechanisms underl... |
| L-ARG-GLY-ASP-SER |
| RGDS |
| fibronectin active fragment |
| L-Arg-Gly-L-Asp-L-Ser-OH |
| RGDS/ARG-GLY-ASP-SER |
| Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser |
| FIBRONECTIN INHIBITOR |
| MFCD00076452 |
| RGDS 1/2ACOH 2H2O |
| H-ARG-GLY-ASP-SER-OH |
| Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-OH |
| R-G-D-S |
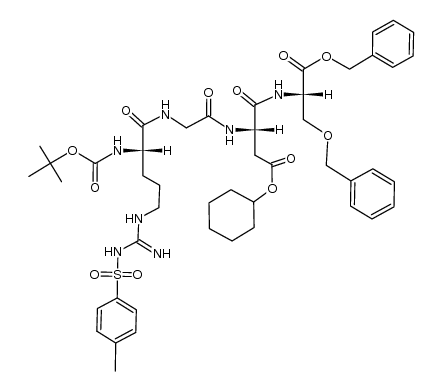 CAS#:199166-39-7
CAS#:199166-39-7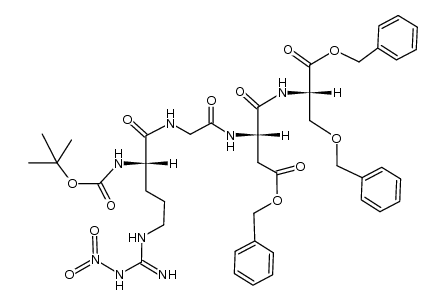 CAS#:246516-47-2
CAS#:246516-47-2 CAS#:63024-02-2
CAS#:63024-02-2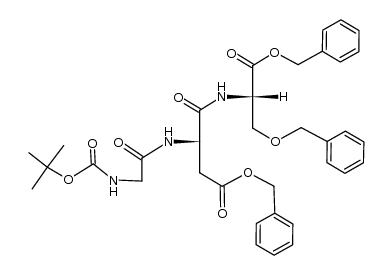 CAS#:143783-29-3
CAS#:143783-29-3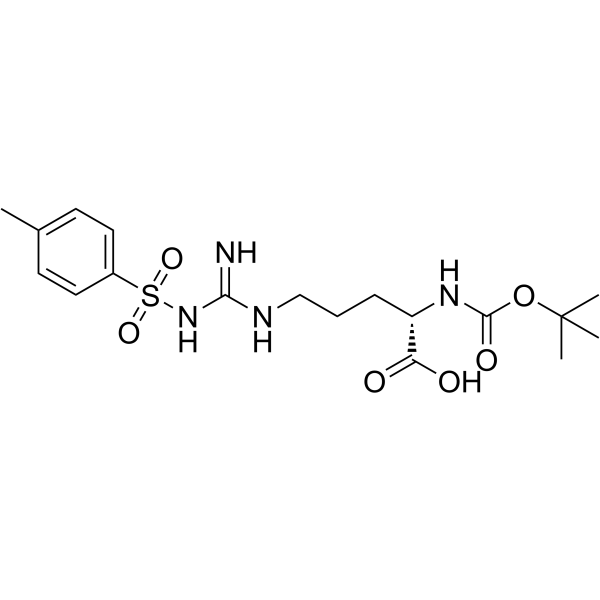 CAS#:13836-37-8
CAS#:13836-37-8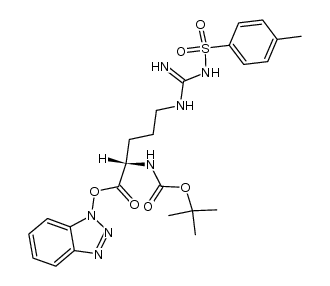 CAS#:105916-77-6
CAS#:105916-77-6 CAS#:788804-09-1
CAS#:788804-09-1
