烟酸
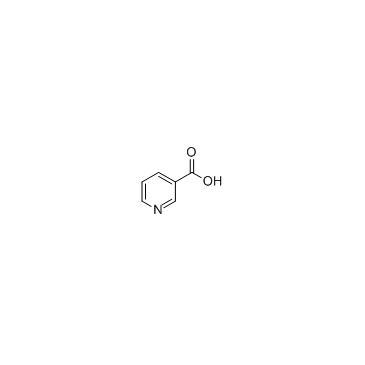
烟酸结构式

|
常用名 | 烟酸 | 英文名 | Nicotinic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 59-67-6 | 分子量 | 123.11 | |
| 密度 | 1.473 | 沸点 | 292.5±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H5NO2 | 熔点 | 234-238 ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 130.7±19.8 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 causes ADAM10-dependent ectodomain shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Mol. Pharmacol. 87(3) , 533-42, (2015) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25D3) has a potential antiatherosclerotic effect through anti-inflammatory actions. We investigated how 1,25D3 regulates tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) expres... |
|
|
Evidence for fatty acids mediating CL 316,243-induced reductions in blood glucose in mice.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 307(7) , E563-70, (2014) CL 316,243, a β3-adrenergic agonist, was developed as an antiobesity and diabetes drug and causes rapid decreases in blood glucose levels in mice. The mechanisms mediating this effect have not been fully elucidated; thus, the purpose of the current study was ... |
|
|
Protein enrichment of an Opuntia ficus-indica cladode hydrolysate by cultivation of Candida utilis and Kluyveromyces marxianus.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(5) , 1094-102, (2015) The cladodes of Opuntia ficus-indica (prickly pear cactus) have a low protein content; for use as a balanced feed, supplementation with other protein sources is therefore desirable. We investigated protein enrichment by cultivation of the yeasts Candida utili... |
|
|
Effect of concentrate feeder design on performance, eating and animal behavior, welfare, ruminal health, and carcass quality in Holstein bulls fed high-concentrate diets.
J. Anim. Sci. 93 , 3018-33, (2015) A total of 240 Holstein bulls (121 ± 2.0 kg initial BW; 99 ± 1.0 d of age), from 2 consecutive fattening cycles, were randomly allocated in 1 of 6 pens and assigned to 1 of the 3 treatments consisting of different concentrate feeder designs: a control feeder ... |
|
|
Solubilization of gliadins for use as a source of nitrogen in the selection of bacteria with gliadinase activity.
Food Chem. 168 , 439-44, (2014) For patients with celiac disease, gliadin detoxification via the use of gliadinases may provide an alternative to a gluten-free diet. A culture medium, in which gliadins were the sole source of nitrogen, was developed for screening for microorganisms with gli... |
|
|
Impact of Taylor-Aris diffusivity on analyte and system zone dispersion in CZE assessed by computer simulation and experimental validation.
Electrophoresis 36 , 1529-38, (2015) Application of pressure-driven laminar flow has an impact on zone and boundary dispersion in open tubular CE. The GENTRANS dynamic simulator for electrophoresis was extended with Taylor-Aris diffusivity which accounts for dispersion due to the parabolic flow ... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
The Japanese toxicogenomics project: application of toxicogenomics.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 54 , 218-27, (2010) Biotechnology advances have provided novel methods for the risk assessment of chemicals. The application of microarray technologies to toxicology, known as toxicogenomics, is becoming an accepted approach for identifying chemicals with potential safety proble... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |