
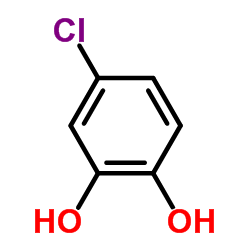
4-氯邻苯二酚结构式

|
常用名 | 4-氯邻苯二酚 | 英文名 | 4-Chlorocatechol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 2138-22-9 | 分子量 | 144.556 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 267.1±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H5ClO2 | 熔点 | 90-94 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 115.3±21.8 °C | |
| 符号 |
GHS05 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Identification of Triclosan-O-Sulfate and other transformation products of Triclosan formed by activated sludge.
Sci. Total Environ. 505 , 39-46, (2014) Aerobic degradation experiments of Triclosan were performed in activated sludge to identify possible transformation products for this compound. During 7 days, the formation of biotransformation products such as 2,4-Dichlorophenol, 4-Chlorocatechol, 5-Hydroxy-... |
|
|
Characterization of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Planococcus sp. strain S5 induced by high phenol concentration.
Acta Biochim. Pol. 59(3) , 345-51, (2012) This study aimed at characterization of a new catechol 2,3-dioxygenase isolated from a Gram-positive bacterium able to utilize phenol as the sole carbon and energy source. Planococcus sp. strain S5 grown on 1 or 2 mM phenol showed activity of both a catechol ... |
|
|
Multistep conversion of para-substituted phenols by phenol hydroxylase and 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenase.
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 169(7) , 2064-75, (2013) A multistep conversion system of para-substituted phenols by recombinant phenol hydroxylase (PH(IND)) and 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenase (BphC(LA-4)) was constructed in this study. Docking studies with different para-substituted phenols and correspondi... |
|
|
Ormosil gels doped with engineered catechol 1,2 dioxygenases for chlorocatechol bioremediation.
Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 61(3) , 297-303, (2014) Enzymes entrapped in wet, nanoporous silica gel have great potential as bioreactors for bioremediation because of their improved thermal, chemical, and mechanical stability with respect to enzymes in solution. The B isozyme of catechol 1,2 dioxygenase from Ac... |
|
|
Role of IncP-1β plasmids pWDL7::rfp and pNB8c in chloroaniline catabolism as determined by genomic and functional analyses.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78(3) , 828-38, (2012) Broad-host-range catabolic plasmids play an important role in bacterial degradation of man-made compounds. To gain insight into the role of these plasmids in chloroaniline degradation, we determined the first complete nucleotide sequences of an IncP-1 chloroa... |
|
|
Characterization of a novel thermostable Mn(II)-dependent 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenase from a polychlorinated biphenyl- and naphthalene-degrading Bacillus sp. JF8.
J. Biol. Chem. 278(24) , 21483-92, (2003) A novel thermostable Mn(II)-dependent 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl-1,2-dioxygenase (BphC_JF8) catalyzing the meta-cleavage of the hydroxylated biphenyl ring was purified from the thermophilic biphenyl and naphthalene degrader, Bacillus sp. JF8, and the gene was clon... |
|
|
Biotransformation of 2,7-dichloro- and 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by Sphingomonas wittichii RW1.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68(5) , 2584-8, (2002) Aerobic biotransformation of the diaryl ethers 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by the dibenzo-p-dioxin-utilizing strain Sphingomonas wittichii RW1, producing corresponding metabolites, was demonstrated for the first time. ... |
|
|
A linear megaplasmid, p1CP, carrying the genes for chlorocatechol catabolism of Rhodococcus opacus 1CP.
Microbiology 150(Pt 9) , 3075-87, (2004) The Gram-positive actinobacterium Rhodococcus opacus 1CP is able to utilize several (chloro)aromatic compounds as sole carbon sources, and gene clusters for various catabolic enzymes and pathways have previously been identified. Pulsed-field gel electrophores... |
|
|
New bacterial pathway for 4- and 5-chlorosalicylate degradation via 4-chlorocatechol and maleylacetate in Pseudomonas sp. strain MT1.
J. Bacteriol. 185(23) , 6790-800, (2003) Pseudomonas sp. strain MT1 is capable of degrading 4- and 5-chlorosalicylates via 4-chlorocatechol, 3-chloromuconate, and maleylacetate by a novel pathway. 3-Chloromuconate is transformed by muconate cycloisomerase of MT1 into protoanemonin, a dominant reacti... |
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain RW41 mineralizes 4-chlorobenzenesulfonate, the major polar by-product from DDT manufacturing.
Environ. Microbiol. 10(6) , 1591-600, (2008) Pseudomonas aeruginosa RW41 is the first bacterial strain, which could be isolated by virtue of its capability to mineralize 4-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid (4CBSA), the major polar by-product of the chemical synthesis of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis-(4-chlorophenyl)... |