2-胍基琥珀酸
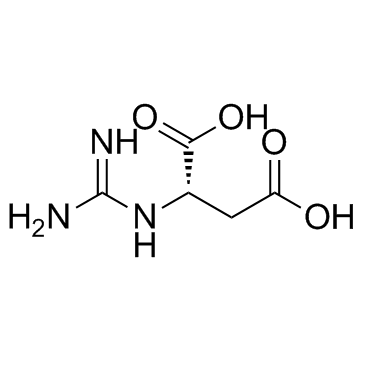
2-胍基琥珀酸结构式

|
常用名 | 2-胍基琥珀酸 | 英文名 | Guanidinosuccinic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 6133-30-8 | 分子量 | 175.143 | |
| 密度 | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 344.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C5H9N3O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 162.1±30.7 °C |
|
Uraemic guanidino compounds inhibit gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked whole cell currents in mouse spinal cord neurones.
Neurosci. Lett. 265(2) , 83-6, (1999) Guanidine, creatinine (CTN), methylguanidine (MG) and guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) are four endogenous guanidino compounds with proven neuroexcitatory actions, and putative pathophysiological significance as uraemic toxins. The effects of these uraemic guanid... |
|
|
Effect of NaCN on currents evoked by uremic retention solutes in dissociated mouse neurons.
Brain Res. 1008(1) , 107-12, (2004) Uremic retention solutes possibly contribute to neuronal hypoxia/ischemia and its consequences in patients with renal failure. We examined the in vitro effects of several uremic retention solutes on murine central neurons under chemically induced metabolic hy... |
|
|
Accumulation of methylguanidine and changes in guanidino compound levels in plasma, urine, and kidneys of furosemide-treated rats.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 57(6) , 802-10, (2008) Antidiuresis and renal diseases alter the levels of guanidino compounds (GCs) in various tissues. Therefore, we hypothesized that diuresis could also disturb GC metabolism, storage, and elimination. In this study, rats were made diuretic to analyze GC levels ... |
|
|
Formation of guanidinosuccinic acid, a stable nitric oxide mimic, from argininosuccinic acid and nitric oxide-derived free radicals.
Free Radic. Res. 31(1) , 59-65, (1999) Guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) is noted for its nitric oxide (NO) mimicking actions such as vasodilatation and activation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. We have reported that GSA is the product of argininosuccinate (ASA) and some reactive oxygen s... |
|
|
First indications demonstrating the preventive effects of NZ-419, a novel intrinsic antioxidant, on the initiation and/or progression of chronic renal failure in rats.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 32(7) , 1204-8, (2009) The concentration of NZ-419 (5-hydroxy-1-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione), an intrinsic antioxidant, has been shown to increase in the sera of animals and patients with chronic renal failure (CRF). This is the first report that orally administered exogenous NZ-... |
|
|
Inhibition of arginine synthesis by urea: a mechanism for arginine deficiency in renal failure which leads to increased hydroxyl radical generation.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 244(1-2) , 11-5, (2003) We have reported that (1) the synthesis of GSA, a uremic toxin, increases depending on the urea concentration and (2) GSA is formed from argininosuccinic acid (ASA) and the hydroxyl radical or SIN-1 which generates superoxide and NO simultaneously. However, a... |
|
|
Methyl group deficiency and guanidino production in uremia.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 244(1-2) , 31-6, (2003) Guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) is one of the earliest uremic toxins isolated and its toxicity identified. Its metabolic origins have remained obscure until recently when a series of studies showed that it arose from the oxidation of argininosuccinic acid (ASA) ... |
|
|
Premature aging in uremia.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 298(1-2) , 195-8, (2007) Guanidinosuccinic acid is an aberrant metabolite isolated 40 years ago in the blood and urine of uremic subjects and a suspect in the toxicity associated with renal failure. It plays a minor role in the bleeding diathesis of uremia, contributes to the methyl ... |
|
|
Methyl group deficiency States.
Nephron 92(1) , 1-6, (2002)
|
|
|
Uremic bleeding: closing the circle after 30 years of controversies?
Blood 94(8) , 2569-74, (1999)
|