1-油酰基-2-乙酰基-sn-丙三醇
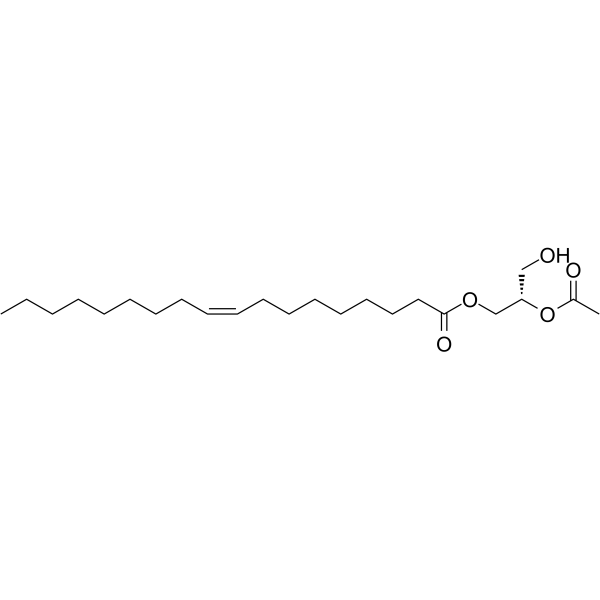
1-油酰基-2-乙酰基-sn-丙三醇结构式

|
常用名 | 1-油酰基-2-乙酰基-sn-丙三醇 | 英文名 | 1-Oleoyl-2-acetyl-rac-glycerol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 86390-77-4 | 分子量 | 398.577 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 490.0±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C23H42O5 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 152.3±13.9 °C |
|
Dopaminergic neurotoxicants cause biphasic inhibition of purinergic calcium signaling in astrocytes.
PLoS ONE 9(11) , e110996, (2014) Dopaminergic nuclei in the basal ganglia are highly sensitive to damage from oxidative stress, inflammation, and environmental neurotoxins. Disruption of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-dependent calcium (Ca2+) transients in astrocytes may represent an important... |
|
|
Calcium sensing receptor modulates extracellular calcium entry and proliferation via TRPC3/6 channels in cultured human mesangial cells.
PLoS ONE 9(6) , e98777, (2014) Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) has been demonstrated to be present in several tissues and cells unrelated to systemic calcium homeostasis, where it regulates a series of diverse cellular functions. A previous study indicated that CaSR is expressed in mouse g... |
|
|
A functional tandem between transient receptor potential canonical channels 6 and calcium-dependent chloride channels in human epithelial cells.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 765 , 337-45, (2015) TRPC6 plays important human physiological functions, notably in artery and arterioles constriction, in regulation of vascular volume and in bronchial muscle constriction. It is implicated in pulmonary hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and focal segmental ... |
|
|
High extracellular Ca2+ stimulates Ca2+-activated Cl- currents in frog parathyroid cells through the mediation of arachidonic acid cascade.
PLoS ONE 6(4) , e19158, (2011) Elevation of extracellular Ca(2+) concentration induces intracellular Ca(2+) signaling in parathyroid cells. The response is due to stimulation of the phospholipase C/Ca(2+) pathways, but the direct mechanism responsible for the rise of intracellular Ca(2+) c... |
|
|
Pleiotropic signaling evoked by tumor necrosis factor in podocytes.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 309 , F98-108, (2015) TNF has been implicated in glomerular diseases, but its actions on podocytes are not well understood. Endogenous TNF expression is markedly increased in mouse podocytes exposed to sera from patients with recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and TNF i... |
|
|
Molecular mechanisms of fMLP-induced superoxide generation and degranulation in mouse neutrophils.
Adv. Biol. Regul. 53(1) , 128-34, (2013) In this manuscript, involvement of PLD in fMLP-induced superoxide generation and degranulation were re-investigated using PLD(-/-) neutrophils, and the molecular mechanisms of these neutrophil functions were examined. Neither PLD1 nor PLD2 is involved in thes... |
|
|
Molecular mechanisms of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced superoxide generation and degranulation in mouse neutrophils: phospholipase D is dispensable.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 33(1) , 136-45, (2013) Phospholipase D (PLD), which produces the lipid messenger phosphatidic acid (PA), has been implicated in superoxide generation and degranulation in neutrophils. The basis for this conclusion is the observation that primary alcohols, which interfere with PLD-c... |
|
|
Derinat Protects Skin against Ultraviolet-B (UVB)-Induced Cellular Damage.
Molecules 20 , 20297-311, (2015) Ultraviolet-B (UVB) is one of the most cytotoxic and mutagenic stresses that contribute to skin damage and aging through increasing intracellular Ca(2+) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Derinat (sodium deoxyribonucleate) has been utilized as an immunomodula... |
|
|
Protein kinase Ctheta negatively regulates store-independent Ca2+ entry and phosphatidylserine exposure downstream of glycoprotein VI in platelets.
J. Biol. Chem. 285(26) , 19865-73, (2010) Platelet activation must be tightly controlled to provide an effective, but not excessive, response to vascular injury. Cytosolic calcium is a critical regulator of platelet function, including granule secretion, integrin activation, and phosphatidylserine (P... |
|
|
High glucose enhances transient receptor potential channel canonical type 6-dependent calcium influx in human platelets via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway.
Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28(4) , 746-51, (2008) Transient receptor potential canonical type 6 (TRPC6) channels mediating 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OAG)-induced calcium entry have been identified on human platelets. In the present study we tested the hypothesis that hyperglycemia increases the expressi... |