一溴二氯甲烷标准溶液
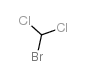
一溴二氯甲烷标准溶液结构式

|
常用名 | 一溴二氯甲烷标准溶液 | 英文名 | BROMODICHLOROMETHANE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 75-27-4 | 分子量 | 163.82900 | |
| 密度 | 1.98 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | 沸点 | 87 °C(lit.) | |
| 分子式 | CHBrCl2 | 熔点 | −55 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 87-89°C | |
| 符号 |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Use of urinary trichloroacetic acid as an exposure biomarker of disinfection by-products in cancer studies.
Environ. Res. 135 , 276-84, (2014) Urinary trichloroacetic acid (TCAA) has been proposed as a valid exposure biomarker for ingested disinfection by-products (DBP) for reproductive studies. However, it has never been used in epidemiologic studies on cancer. We investigate the performance of uri... |
|
|
Development of QSAR models for predicting hepatocarcinogenic toxicity of chemicals.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44 , 3658-64, (2009) A dataset comprising 55 chemicals with hepatocarcinogenic potency indices was collected from the Carcinogenic Potency Database with the aim of developing QSAR models enabling prediction of the above unwanted property for New Chemical Entities. The dataset was... |
|
|
Comparing a silver-impregnated activated carbon with an unmodified activated carbon for disinfection by-product minimisation and precursor removal.
Sci. Total Environ. 542 , 672-84, (2015) During disinfection, bromide, iodide and natural organic matter (NOM) in source waters can lead to the formation of brominated and/or iodinated disinfection by-products (DBPs), which are often more toxic than their chlorinated analogues. The objective of this... |
|
|
Reverse dosimetry: interpreting trihalomethanes biomonitoring data using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling.
J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 17(7) , 591-603, (2007) Biomonitoring data provide evidence of exposure of environmental chemicals but are not, by themselves, direct measures of exposure. To use biomonitoring data in understanding exposure, physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling can be used in a rev... |
|
|
CYP2E1-dependent and leptin-mediated hepatic CD57 expression on CD8+ T cells aid progression of environment-linked nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 274(1) , 42-54, (2014) Environmental toxins induce a novel CYP2E1/leptin signaling axis in liver. This in turn activates a poorly characterized innate immune response that contributes to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) progression. To identify the relevant subsets of T-lymphocy... |
|
|
DNA damage and micronuclei induced in rat and human kidney cells by six chemicals carcinogenic to the rat kidney.
Toxicology 204(2-3) , 187-95, (2004) Six chemicals, known to induce kidney tumors in rats, were examined for their ability to induce DNA fragmentation and formation of micronuclei in primary cultures of rat and human kidney cells, and in the kidney of intact rats. Significant dose-dependent incr... |
|
|
Disposition of bromodichloromethane in humans following oral and dermal exposure.
Toxicol. Sci. 99(2) , 432-45, (2007) Exposure to bromodichloromethane (BDCM), one of the most prevalent disinfection byproducts in drinking water, can occur via ingestion of water and by dermal absorption and inhalation during activities such as bathing and showering. The objectives of this rese... |
|
|
Multi-route trihalomethane exposure in households using municipal tap water treated with chlorine or ozone-chlorine.
Sci. Total Environ. 339(1-3) , 143-52, (2005) In Korea, data for multi-route trihalomethane (THM) exposure in households using municipal tap water treated with ozone-chlorine or chlorine are unavailable or very limited. Accordingly, the present study was designed to obtain those data by measurements of t... |
|
|
Modeling daily variation of trihalomethane compounds in drinking water system, Houston, Texas.
J. Hazard. Mater. 151(2-3) , 662-8, (2008) Total trihalomethanes (TTHM) concentrations vary widely and periodically between 70 and 130 ppb. Data from the National Environmental Services Laboratory, Houston, Texas indicate that pH and free residual chlorine contribute minimally to the wide variability ... |
|
|
Sensitive headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination of trihalomethanes in urine.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 848(2) , 277-82, (2007) A sensitive and straightforward method for the determination of trihalomethanes (THMs) in urine by using headspace extraction technique has been developed. Chemical and instrumental variables were studied in order to optimize the method for sensitivity: an ex... |