2-丁烯腈
一般危化品
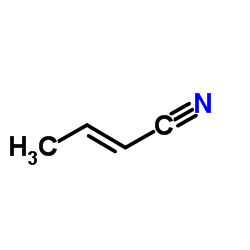
2-丁烯腈结构式
|
常用名 | 2-丁烯腈 | 英文名 | crotononitrile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 4786-20-3 | 分子量 | 67.089 | |
| 密度 | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 120.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C4H5N | 熔点 | -51.5ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 20.0±0.0 °C | |
| 符号 |


GHS02, GHS07 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Comparative developmental toxicities of aliphatic nitriles: in vivo and in vitro observations.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 163(2) , 149-63, (2000) The effects on embryonic development of a series of eight saturated (acetonitrile, propionitrile, and n-butyronitrile) and unsaturated (acrylonitrile, methacrylonitrile, allylnitrile, cis-2-pentenenitrile, and 2-chloroacrylonitrile) nitriles were compared in ... |
|
|
A new unifying hypothesis for lathyrism, konzo and tropical ataxic neuropathy: nitriles are the causative agents.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 49(3) , 563-70, (2011) Konzo and lathyrism are associated with consumption of cassava and grass pea, respectively. Cassava consumption has also been associated with a third disease, tropical ataxic neuropathy (TAN). This review presents a new unifying hypothesis on the causative ag... |
|
|
Relative developmental toxicities of inhaled aliphatic mononitriles in rats.
Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 20(3) , 365-75, (1993) The developmental toxicities of eight aliphatic mononitriles were studied in Sprague-Dawley rats after inhalation exposure for 6 hr/day, during Days 6 to 20 of gestation. The range of exposure concentrations for acetonitrile was 900 to 1800 ppm; for propionit... |
|
|
Differential effects of trans-crotononitrile and 3-acetylpyridine on inferior olive integrity and behavioural performance in the rat.
Eur. J. Neurosci. 22(4) , 880-94, (2005) The inferior olive climbing fibre projection is key to cerebellar contributions to motor control. Here we present evidence for a novel tool, trans-crotononitrile (TCN), to selectively inactivate the olive to study its functions. Anatomical, electrophysiologic... |
|
|
The behavioral syndrome caused by 3,3'-iminodipropionitrile and related nitriles in the rat is associated with degeneration of the vestibular sensory hair cells.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 123(2) , 199-210, (1993) Animals exposed to 3,3'-iminodipropionitrile (IDPN) or to several similar nitriles develop a permanent syndrome of behavioral abnormalities. The present work addressed the hypothesis that this syndrome is caused by a toxic effect of these nitriles on the peri... |
|
|
[Allylnitrile-induced behavioral abnormalities and findings relating to the mechanism underlying behavioral abnormalities].
Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 54(2) , 459-66, (1999) Nitriles are widely used in industry as plastics, solvents, and synthetic intermediates. It has been shown that the thermal degradation of acrylonitrile-based plastics leads to the emission of a great variety of nitriles. Exposure of humans and experimental a... |
|
|
The ototoxic effects induced in rats by treatment for 12 weeks with 2-butenenitrile, 3-butenenitrile and cis-2-pentenenitrile.
Pharmacol. Toxicol. 88(3) , 126-34, (2001) Brainstem auditory and visual evoked-potentials were studied in male Sprague-Dawley rats during subchronic oral treatment with three unsaturated aliphatic nitriles. The rats were given, by gastric intubation, doses of 10, 20 and 40 mg x kg(-1) 3-butenenitrile... |
|
|
Degeneration and gliosis in rat retina and central nervous system following 3,3'-iminodipropionitrile exposure.
Brain Res. 833(2) , 258-71, (1999) 3,3'-Iminodipropionitrile (IDPN) exposure causes a neurofilamentous axonopathy and olfactory, audiovestibular and visual toxicity. Many events relevant to these effects and the neurotoxic properties of nitriles as a class remain to be elucidated. We character... |
|
|
Butenenitriles have low axonopathic potential in the rat.
Toxicol. Lett. 200(3) , 187-93, (2011) IDPN (3,3'-iminodipropionitrile) causes a neurofilamentous proximal axonopathy. This study addressed the hypothesis that the butenenitriles (allylnitrile, cis-crotononitrile and trans-crotononitrile) have an IDPN-like axonopathic potential. First, male adult ... |
|
|
Behavioral abnormalities and apoptotic changes in neurons in mice brain following a single administration of allylnitrile.
Arch. Toxicol. 73(1) , 22-32, (1999) A single dose of allylnitrile in mice might induce persistent behavioral abnormalities, of which the mechanism is not yet known. The present study was undertaken to explore the relationship between behavioral abnormalities and pathological changes in the brai... |