N-Acetylimidoquinone
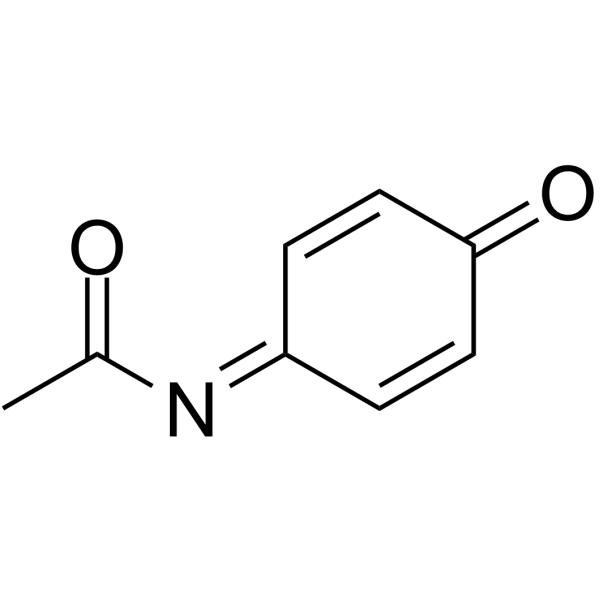
N-Acetylimidoquinone structure
|
Common Name | N-Acetylimidoquinone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50700-49-7 | Molecular Weight | 149.147 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 255.6±43.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7NO2 | Melting Point | 74-75ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 101.6±33.5 °C | |
Use of N-AcetylimidoquinoneNAPQI is the toxic metabolite of Paracetamol. NAPQI is also an inhibitor of enzymes in the vitamin K cycle. NAPQI is rapidly detoxified by glutathione (GSH), but in situations of GSH deficiency, excess NAPQI reacts with cysteine residues in proteins, causing cell death and toxicity in the liver[1][2]. |
| Name | N-acetyl-1,4-benzoquinone imine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | NAPQI is the toxic metabolite of Paracetamol. NAPQI is also an inhibitor of enzymes in the vitamin K cycle. NAPQI is rapidly detoxified by glutathione (GSH), but in situations of GSH deficiency, excess NAPQI reacts with cysteine residues in proteins, causing cell death and toxicity in the liver[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 255.6±43.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 74-75ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 149.147 |
| Flash Point | 101.6±33.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 149.047684 |
| PSA | 46.50000 |
| LogP | 0.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AC6960000 |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Targeting mitochondria with methylene blue protects mice against acetaminophen-induced liver injury.
Hepatology 61(1) , 326-36, (2015) Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is a frequent cause of drug-induced liver injury and the most frequent cause of acute liver failure in the Western world. Previous studies with mouse models have revealed... |
|
|
Monitoring paracetamol metabolism after single and repeated administration in pediatric patients with neoplastic diseases.
Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 45(9) , 496-503, (2007) Paracetamol (PCM) is frequently used in pediatric patients with neoplastic disease. It is metabolized mainly by conjugation, but at therapeutic concentrations, a small fraction of the drug undergoes o... |
|
|
Use of a systems model of drug-induced liver injury (DILIsym®) to elucidate the mechanistic differences between acetaminophen and its less-toxic isomer, AMAP, in mice
Toxicol. Lett. 226(2) , 163-72, (2014) Acetaminophen (APAP) has been used as a probe drug to investigate drug-induced liver injury (DILI). In mice, 3′-hydroxyacetanilide (AMAP), a less-toxic isomer of APAP, has also been studied as a negat... |
| Acetimidoquinone |
| N-Acetyl-1,4-benzoquinone imine |
| N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinonimine |
| p-benzoquinonimine, N-acetyl- |
| N-(4-Oxo-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene)acetamide |
| N-Acetyl-P-benzoquinoneimine |
| N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone Imine |
| N-acetyl-4-benzoquinoneimine |
| Acetamide, N-(4-oxo-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene)- |
| N-(4-Oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)acetamide |
| NAPQI |
| N-(4-Oxo-1-cyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene)acetamide,N-Acetyl-p-benzo-quinoneimine,NAPQI |
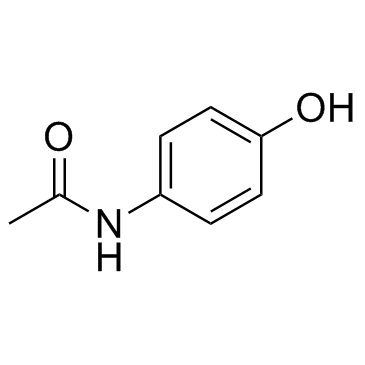
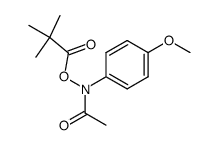

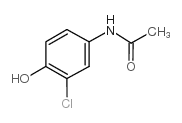

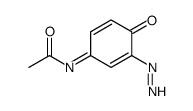
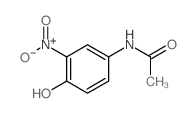
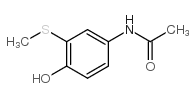 CAS#:37398-23-5
CAS#:37398-23-5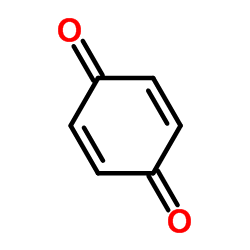 CAS#:106-51-4
CAS#:106-51-4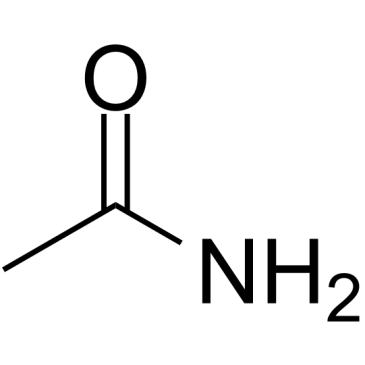 CAS#:60-35-5
CAS#:60-35-5 CAS#:7403-75-0
CAS#:7403-75-0