L-精氨酸
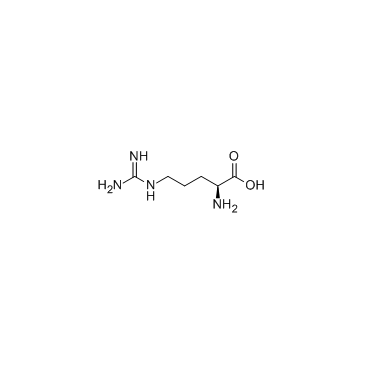
L-精氨酸结构式

|
常用名 | L-精氨酸 | 英文名 | L-arginine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 74-79-3 | 分子量 | 174.201 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 367.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H14N4O2 | 熔点 | 222 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 176.1±30.7 °C |
|
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) protease: a chymotrypsin-like enzyme that processes both non-structural (pORF1) and capsid (pORF2) protein.
J. Gen. Virol. 95(Pt 8) , 1689-700, (2014) Hepatitis E virus (HEV), a major cause of acute viral hepatitis across the world, is a non-enveloped, plus-strand RNA virus. Its genome codes three proteins, pORF1 (multifunctional polyprotein), pORF2 (capsid protein) and pORF3 (multi-regulatory protein). pOR... |
|
|
Mechanistic studies on the flavin-dependent N⁶-lysine monooxygenase MbsG reveal an unusual control for catalysis.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 550-551 , 58-66, (2014) The mechanism of Mycobacterium smegmatis G (MbsG), a flavin-dependent l-lysine monooxygenase, was investigated under steady-state and rapid reaction conditions using primary and solvent kinetic isotope effects, substrate analogs, pH and solvent viscosity effe... |
|
|
Sustained Arginase 1 Expression Modulates Pathological Tau Deposits in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 14842-60, (2015) Tau accumulation remains one of the closest correlates of neuronal loss in Alzheimer's disease. In addition, tau associates with several other neurodegenerative diseases, collectively known as tauopathies, in which clinical phenotypes manifest as cognitive im... |
|
|
Down regulation of NO signaling in Trypanosoma cruzi upon parasite-extracellular matrix interaction: changes in protein modification by nitrosylation and nitration.
PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9 , e0003683, (2015) Adhesion of the Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes, the causative agent of Chagas' disease in humans, to components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) is an important step in host cell invasion. The signaling events triggered in the parasite upon binding to ECM... |
|
|
Cmr1/WDR76 defines a nuclear genotoxic stress body linking genome integrity and protein quality control.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6533, (2015) DNA replication stress is a source of genomic instability. Here we identify changed mutation rate 1 (Cmr1) as a factor involved in the response to DNA replication stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and show that Cmr1--together with Mrc1/Claspin, Pph3, the cha... |
|
|
Remineralization efficacy of a toothpaste containing 8% arginine and calcium carbonate on enamel surface.
Am. J. Dent. 26(5) , 291-7, (2013) To investigate the remineralization efficacy of different types of toothpastes on initial enamel lesions in vitro.Artificial initial lesions were created on 150 enamel discs from freshly extracted bovine incisors. These enamel discs were divided into five gro... |
|
|
An improved ARS2-derived nuclear reporter enhances the efficiency and ease of genetic engineering in Chlamydomonas.
Biotechnol. J. 10(3) , 473-9, (2015) The model alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has been used to pioneer genetic engineering techniques for high-value protein and biofuel production from algae. To date, most studies of transgenic Chlamydomonas have utilized the chloroplast genome due to its ease o... |
|
|
Defining the property space for chromatographic ligands from a homologous series of mixed-mode ligands.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1407 , 58-68, (2015) A homologous ligand library based on the commercially-available Nuvia cPrime ligand was generated to systematically explore various features of a multimodal cation-exchange ligand and to identify structural variants that had significantly altered chromatograp... |
|
|
Impact of Taylor-Aris diffusivity on analyte and system zone dispersion in CZE assessed by computer simulation and experimental validation.
Electrophoresis 36 , 1529-38, (2015) Application of pressure-driven laminar flow has an impact on zone and boundary dispersion in open tubular CE. The GENTRANS dynamic simulator for electrophoresis was extended with Taylor-Aris diffusivity which accounts for dispersion due to the parabolic flow ... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |