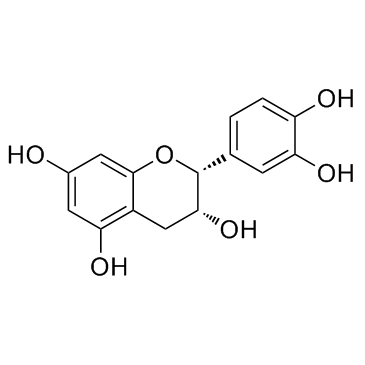
茶黄素

茶黄素结构式

|
常用名 | 茶黄素 | 英文名 | Theaflavin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 4670-05-7 | 分子量 | 564.49 | |
| 密度 | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 926.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C29H24O12 | 熔点 | 240 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 314.3±27.8 °C |
茶黄素用途Theaflavin 是一种天然的甲型流感 (H1N1) 神经氨酸酶抑制剂。 |
| 中文名 | 茶黄素 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 3,4,5-trihydroxy-1,8-bis[(2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]benzo[7]annulen-6-one |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Theaflavin 是一种天然的甲型流感 (H1N1) 神经氨酸酶抑制剂。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点实验 |
Influenza A (H1N1) virus[1] |
| 体外研究 | 在绿茶中发现的茶黄素被观察到抑制由最低对接能量强烈支持的H1N1 NA蛋白。茶黄素是传统上用于治疗流感感染的植物产品。绿茶特别富含多种酚类化合物,如茶黄素。茶黄素衍生物显示出显着的抗病毒活性。发现茶黄素通过形成氢键与NA的Arg118,Asp151,Asp 152,Arg193,Asp199,Asn344和Arg430等氨基酸残基相互作用[1]。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 926.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 240 °C |
| 分子式 | C29H24O12 |
| 分子量 | 564.49 |
| 闪点 | 314.3±27.8 °C |
| PSA | 156.91000 |
| LogP | 1.61 |
| InChIKey | IPMYMEWFZKHGAX-ZKSIBHASSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1c(O)cc(C2Oc3cc(O)cc(O)c3CC2O)cc2c(C3Oc4cc(O)cc(O)c4CC3O)cc(O)c(O)c12 |
| 外观性状 | 固体;Red to Dark red to Brown powder to crystal |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.760 |
| 储存条件 | 常温,避光,通风干燥处,密封保存 |
| 稳定性 | 常温常压下稳定 |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:133.99 2、 摩尔体积(m3/mol):325.7 3、 等张比容(90.2K):1000.5 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):88.9 5、 极化率(10 -24cm 3):53.11 |
| 计算化学 | 1、 疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):0.6 2、 氢键供体数量:9 3、 氢键受体数量:12 4、 可旋转化学键数量:2 5、 互变异构体数量:998 6、 拓扑分子极性表面积(TPSA):218 7、 重原子数量:41 8、 表面电荷:0 9、 复杂度:1260 10、 同位素原子数量:0 11、 确定原子立构中心数量:4 12、 不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13、 确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14、 不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15、 共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:不确定 2. 密度(g/mL,25 ºC):不确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):不确定 4. 熔点(ºC):不确定 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):不确定 6. 沸点(ºC,21mmHg):不确定 7. 折射率:不确定 8. 闪点(ºF):不确定 9. 比旋光度(º,C=1, H2O):不确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):不确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):不确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):不确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):不确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):不确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):不确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:不确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):不确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):不确定 19. 溶解性:不确定 |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | 24/25 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| 海关编码 | 3203001990 |
|
~15% 
茶黄素 4670-05-7 |
| 文献:Jhoo, Jin-Woo; Lo, Chih-Yu; Li, Shiming; Sang, Shengmin; Ang, Catharina Y. W.; Heinze, Thomas M.; Ho, Chi-Tang Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 53, # 15 p. 6146 - 6150 |
|
~40% 
茶黄素 4670-05-7 |
| 文献:Chemical Communications, , # 15 p. 1365 - 1366 |
|
~% 
茶黄素 4670-05-7 |
| 文献:Kawabe, Yusuke; Aihara, Yoshiyuki; Hirose, Yoshitsugu; Sakurada, Asuka; Yoshida, Atsushi; Inai, Makoto; Asakawa, Tomohiro; Hamashima, Yoshitaka; Kan, Toshiyuki Synlett, 2013 , vol. 24, # 4 art. no. ST-2012-U1061-L, p. 479 - 482 |
|
~%
详细
|
| 文献:Journal of Natural Products, , vol. 73, # 1 p. 33 - 39 |
| 茶黄素上游产品 3 | |
|---|---|
| 茶黄素下游产品 0 | |
| 海关编码 | 3203001990 |
|---|
|
Theaflavins, dimeric catechins, inhibit peptide transport across Caco-2 cell monolayers via down-regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated peptide transporter PEPT1.
Food Chem. 138(4) , 2140-5, (2013) In the small intestine, peptide transporter 1 (PEPT1) plays a role in the transport of di- and tripeptides. In this study, we investigated whether theaflavins (TFs) affect the absorption of small pept... |
|
|
Polyphenols extracted from black tea (Camellia sinensis) residue by hot-compressed water and their inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase in vitro.
J. Food Sci. 77(12) , H254-61, (2012) Polyphenols, retained in black tea wastes following the commercial production of tea beverages, represent an underutilized resource. The purpose of this study was to investigate the potential use of h... |
|
|
Therapeutic attenuation of neuroinflammation and apoptosis by black tea theaflavin in chronic MPTP/probenecid model of Parkinson's disease.
Neurotox. Res. 23(2) , 166-73, (2013) Neuroinflammation and apoptosis in the dopaminergic neurons of substantia nigra play an important role in the pathogenesis of experimental and clinical Parkinson's disease (PD). This study focused on ... |
| Theaflavine |
| Theaflavin |
| 1,8-Bis[(2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]-5H-benzo[7]annulen-5-one |




![(5S,10S)-1,2,8,9,10-pentahydroxy-4,6,13-tris((2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxychroman-2-yl)-5,10-dihydro-11H-5,10-ethenodibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-11-one结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/454/1204351-30-3.png)


