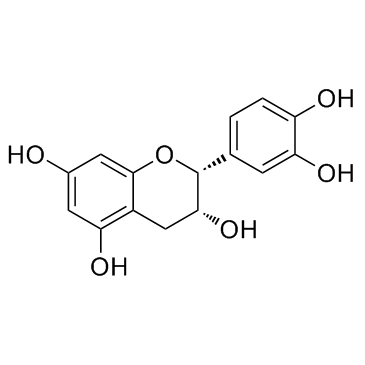
Theaflavin

Theaflavin structure
|
Common Name | Theaflavin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4670-05-7 | Molecular Weight | 564.49 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 926.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H24O12 | Melting Point | 240 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 314.3±27.8 °C | |
Use of TheaflavinTheaflavin is a suitable natural inhibitor against influenza A (H1N1) neuraminidase. |
| Name | 3,4,5-trihydroxy-1,8-bis[(2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]benzo[7]annulen-6-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Theaflavin is a suitable natural inhibitor against influenza A (H1N1) neuraminidase. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Influenza A (H1N1) virus[1] |
| In Vitro | Theaflavin, found in green tea, is observed to inhibit H1N1 NA proteins strongly supported by lowest docking energy. Theaflavin is a plant product traditionally used for treatment of influenza infection. Green tea is particularly rich in polyphenolic compounds like Theaflavin. Theaflavin derivatives have shown pronounced antiviral activity. Theaflavin is found to interact with the amino acid residues like Arg118, Asp151, Asp 152, Arg193, Asp199, Asn344, and Arg430 of NA by forming hydrogen bonds[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 926.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 240 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C29H24O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 564.49 |
| Flash Point | 314.3±27.8 °C |
| PSA | 156.91000 |
| LogP | 1.61 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.760 |
| InChIKey | IPMYMEWFZKHGAX-ZKSIBHASSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1c(O)cc(C2Oc3cc(O)cc(O)c3CC2O)cc2c(C3Oc4cc(O)cc(O)c4CC3O)cc(O)c(O)c12 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 3203001990 |
|
~15% 
Theaflavin CAS#:4670-05-7 |
| Literature: Jhoo, Jin-Woo; Lo, Chih-Yu; Li, Shiming; Sang, Shengmin; Ang, Catharina Y. W.; Heinze, Thomas M.; Ho, Chi-Tang Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 53, # 15 p. 6146 - 6150 |
|
~40% 
Theaflavin CAS#:4670-05-7 |
| Literature: Chemical Communications, , # 15 p. 1365 - 1366 |
|
~% 
Theaflavin CAS#:4670-05-7 |
| Literature: Kawabe, Yusuke; Aihara, Yoshiyuki; Hirose, Yoshitsugu; Sakurada, Asuka; Yoshida, Atsushi; Inai, Makoto; Asakawa, Tomohiro; Hamashima, Yoshitaka; Kan, Toshiyuki Synlett, 2013 , vol. 24, # 4 art. no. ST-2012-U1061-L, p. 479 - 482 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Journal of Natural Products, , vol. 73, # 1 p. 33 - 39 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 3203001990 |
|---|
|
Theaflavins, dimeric catechins, inhibit peptide transport across Caco-2 cell monolayers via down-regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated peptide transporter PEPT1.
Food Chem. 138(4) , 2140-5, (2013) In the small intestine, peptide transporter 1 (PEPT1) plays a role in the transport of di- and tripeptides. In this study, we investigated whether theaflavins (TFs) affect the absorption of small pept... |
|
|
Polyphenols extracted from black tea (Camellia sinensis) residue by hot-compressed water and their inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase in vitro.
J. Food Sci. 77(12) , H254-61, (2012) Polyphenols, retained in black tea wastes following the commercial production of tea beverages, represent an underutilized resource. The purpose of this study was to investigate the potential use of h... |
|
|
Therapeutic attenuation of neuroinflammation and apoptosis by black tea theaflavin in chronic MPTP/probenecid model of Parkinson's disease.
Neurotox. Res. 23(2) , 166-73, (2013) Neuroinflammation and apoptosis in the dopaminergic neurons of substantia nigra play an important role in the pathogenesis of experimental and clinical Parkinson's disease (PD). This study focused on ... |
| Theaflavine |
| Theaflavin |
| 5H-Benzocyclohepten-5-one, 1,8-bis[(2R,3R)-3,4-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2-yl]- |
| 1,8-Bis[(2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]-5H-benzo[7]annulen-5-one |



![(5S,10S)-1,2,8,9,10-pentahydroxy-4,6,13-tris((2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxychroman-2-yl)-5,10-dihydro-11H-5,10-ethenodibenzo[a,d][7]annulen-11-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/454/1204351-30-3.png)

