Albendazole
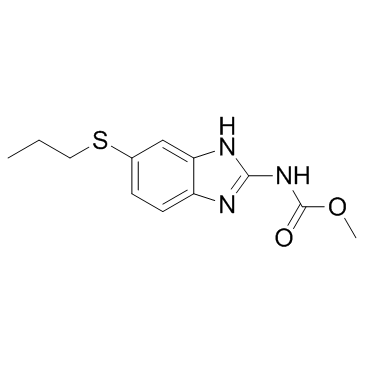
Albendazole structure
|
Common Name | Albendazole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 54965-21-8 | Molecular Weight | 265.331 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H15N3O2S | Melting Point | 207-211°C(分解) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Microtubule disruption synergizes with oncolytic virotherapy by inhibiting interferon translation and potentiating bystander killing.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6410, (2015) In this study, we show that several microtubule-destabilizing agents used for decades for treatment of cancer and other diseases also sensitize cancer cells to oncolytic rhabdoviruses and improve therapeutic outcomes in resistant murine cancer models. Drug-in... |
|
|
Phenotypic and genotypic characterisation of Haemonchus spp. and other gastrointestinal nematodes resistant to benzimidazole in infected calves from the tropical regions of Campeche State, Mexico.
Vet. Parasitol. 205(1-2) , 246-54, (2014) The aim of this study was to identify the presence of anthelmintic resistance to benzimidazole (BZ) in gastrointestinal nematodes (GIN) from naturally infected calves in the tropical regions of Campeche State of Mexico. The faecal egg count reduction test (FE... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Investigation of the complexation of albendazole with cyclodextrins for the design of new antiparasitic formulations
Carbohydr. Res. 398 , 50-5, (2014) Graphical abstract Representation of the complex between ABZ (cyan) and Me-β-CD (yellow) obtained by molecular docking (1:1 stoichiometry). Surfaces colored in yellow and cyan represent solvent accessible surfaces for Me-β-CD and ABZ, respectively. Views from... |
|
|
A combination turbidity and supernatant microplate assay to rank-order the supersaturation limits of early drug candidates.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(10) , 3022-32, (2014) A unique opportunity exists at the drug discovery stage to overcome inherently poor solubility by selecting drug candidates with superior supersaturation propensity. Existing supersaturation assays compare either precipitation-resistant or precipitation-inhib... |
|
|
Development of a phospholipidosis database and predictive quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models.
Toxicol. Mech. Methods 18 , 217-27, (2008) ABSTRACT Drug-induced phospholipidosis (PL) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of phospholipids and drug in lysosomes, and is found in a variety of tissue types. PL is frequently manifested in preclinical studies and may delay or prevent the dev... |
|
|
The effect of metronidazole on the cell cycle and DNA in metronidazole-susceptible and -resistant Giardia cell lines.
Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 198(2) , 75-81, (2015) Metronidazole (MTZ) is used as the drug of choice to treat Giardia infections. It is believed that the prodrug is transformed intracellularly into toxic intermediates that interact with cellular components, leading to cell death. The present study aimed to de... |