Ampicillin sodium
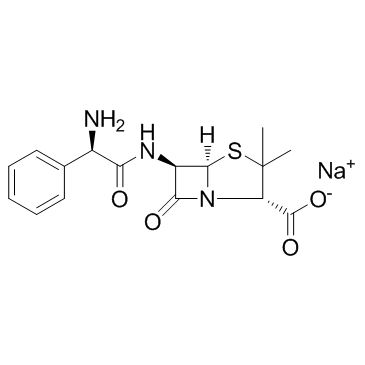
Ampicillin sodium structure
|
Common Name | Ampicillin sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69-52-3 | Molecular Weight | 371.387 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 683.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H18N3NaO4S | Melting Point | 215 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Glucose recognition proteins for glucose sensing at physiological concentrations and temperatures.
ACS Chem. Biol. 9(7) , 1595-602, (2014) Advancements in biotechnology have allowed for the preparation of designer proteins with a wide spectrum of unprecedented chemical and physical properties. A variety of chemical and genetic methods can be employed to tailor the protein's properties, including... |
|
|
Phenotypic heterogeneity enables uropathogenic Escherichia coli to evade killing by antibiotics and serum complement.
Infect. Immun. 83(3) , 1056-67, (2015) Uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli (UPEC) are the major cause of bacteremic urinary tract infections. Survival in the bloodstream is associated with different mechanisms that help to resist serum complement-mediated killing. While the phenotypic hetero... |
|
|
Anti-tumor effects of flavonoids from the ethnic medicine Docynia delavayi (Franch.) Schneid. and its possible mechanism.
J. Med. Food 17(7) , 787-94, (2014) This study investigated the active components and the anti-tumor efficacy and mechanisms of the flavonoids from Docynia delavayi (Franch.) Schneid. (DDS). MTT assay was used to examine the growth inhibitory effects of the four flavonoids, including chrysin, q... |
|
|
Synthesis and accumulation of aromatic aldehydes in an engineered strain of Escherichia coli.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(33) , 11644-54, (2014) Aromatic aldehydes are useful in numerous applications, especially as flavors, fragrances, and pharmaceutical precursors. However, microbial synthesis of aldehydes is hindered by rapid, endogenous, and redundant conversion of aldehydes to their corresponding ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Antibacterial compounds from Salvia adenophora Fernald (Lamiaceae).
Phytochemistry 110 , 120-32, (2015) From the aerial parts of Salvia adenophora Fernald four derivatives of 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (1-4) together with five clerodane diterpenoids (5, 6, 8-10), and one known diterpene (7) have been isolated. Compounds 1-6 and 8-10 are described for the first ti... |
|
|
Role of substituents on the reactivity and product selectivity in reactions of naphthalene derivatives catalyzed by the orphan thermostable cytochrome P450, CYP175A1.
Bioorg. Chem. 62 , 94-105, (2015) The thermostable nature of CYP175A1 enzyme is of potential interest for the biocatalysis at ambient temperature or at elevated temperature under environmentally benign conditions. Although little is known about the substrate selectivity of this enzyme, the bi... |
|
|
Early empiric antibiotic use in preterm infants is associated with lower bacterial diversity and higher relative abundance of Enterobacter.
J. Pediatr. 165(1) , 23-9, (2014) To determine the impact of empiric ampicillin and gentamicin use in the first week of life on microbial colonization and diversity in preterm infants.The 16s ribosomal DNA community profiling was used to compare the microbiota of 74 infants born ≤32 weeks ges... |
|
|
An improved selective culture medium enhances the isolation of Burkholderia pseudomallei from contaminated specimens.
Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 89(5) , 973-82, (2013) Burkholderia pseudomallei is a Gram-negative environmental bacterium found in tropical climates that causes melioidosis. Culture remains the diagnostic gold standard, but isolation of B. pseudomallei from heavily contaminated sites, such as fecal specimens, c... |
|
|
A protocol for the production of recombinant spider silk-like proteins for artificial fiber spinning.
Nat. Protoc. 4 , 341-55, (2009) The extreme strength and elasticity of spider silks originate from the modular nature of their repetitive proteins. To exploit such materials and mimic spider silks, comprehensive strategies to produce and spin recombinant fibrous proteins are necessary. This... |