2-Thiophenecarbohydrazide
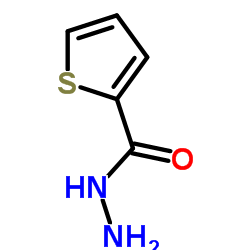
2-Thiophenecarbohydrazide structure
|
Common Name | 2-Thiophenecarbohydrazide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2361-27-5 | Molecular Weight | 142.179 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 260ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H6N2OS | Melting Point | 136-139 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 117.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A minimalist biosensor: Quantitation of cyclic di-GMP using the conformational change of a riboswitch aptamer.
RNA Biol. 12 , 1189-97, (2015) Cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) is a second messenger that is important in regulating bacterial physiology and behavior, including motility and virulence. Many questions remain about the role and regulation of this signaling molecule, but current methods of detectio... |
|
|
Synthetic Long Peptide Derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis Latency Antigen Rv1733c Protects against Tuberculosis.
Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 22 , 1060-9, (2015) Responsible for 9 million new cases of active disease and nearly 2 million deaths each year, tuberculosis (TB) remains a global health threat of overwhelming dimensions. Mycobacterium bovis BCG, the only licensed vaccine available, fails to confer lifelong pr... |
|
|
A novel inhibitor of gyrase B is a potent drug candidate for treatment of tuberculosis and nontuberculosis mycobacterial infections.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59(3) , 1455-65, (2015) New drugs to treat drug-resistant tuberculosis are urgently needed. Extensively drug-resistant and probably the totally drug-resistant tuberculosis strains are resistant to fluoroquinolones like moxifloxacin, which target gyrase A, and most people infected wi... |
|
|
The in vivo expressed Mycobacterium tuberculosis (IVE-TB) antigen Rv2034 induces CD4⁺ T-cells that protect against pulmonary infection in HLA-DR transgenic mice and guinea pigs.
Vaccine 32(29) , 3580-8, (2014) Tuberculosis (TB) remains a life-threatening infectious disease of global proportions with serious negative health and economic consequences. The lack of sufficient protection induced by Mycobacterium bovis BCG, the current vaccine for TB, as well as the impa... |
|
|
Rapid preliminary differentiation of species within the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex: proposition of a radiometric method.
Res. Microbiol. 142(6) , 659-65, (1991) A radiometric method using the "Bactec 460-TB" apparatus now enables rapid obtaining of drug-susceptibility data and differentiation of clinical mycobacterial specimens into those belonging to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (comprised of M. tuberculos... |
|
|
Taxonomic studies on the Mycobacterium tuberculosis series.
Microbiol. Immunol. 29(4) , 285-99, (1985) Numerical classification of slowly growing mycobacteria, including 159 strains received as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. africanum, and M. microti, was carried out using 88 characters, and the following results were obtained. 1) All 159 strains rec... |
|
|
Repeated Aerosolized-Boosting with Gamma-Irradiated Mycobacterium bovis BCG Confers Improved Pulmonary Protection against the Hypervirulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strain HN878 in Mice.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0141577, (2015) Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), the only licensed vaccine, shows limited protection efficacy against pulmonary tuberculosis (TB), particularly hypervirulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) strains, suggesting that a logistical and practic... |
|
|
Crystal structures of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase genotype 2a of hepatitis C virus reveal two conformations and suggest mechanisms of inhibition by non-nucleoside inhibitors.
J. Biol. Chem. 280(18) , 18202-10, (2005) Crystal structures of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase genotype 2a of hepatitis C virus (HCV) from two crystal forms have been determined. Similar to the three-dimensional structures of HCV polymerase genotype 1b and other known polymerases, the structures of... |
|
|
Subdivision of Mycobacterium tuberculosis into five variants for epidemiological purposes: methods and nomenclature.
J. Hyg. (Lond) 89(2) , 235-42, (1982) Virulent strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated from humans are divisible into five variants by using four tests: oxygen requirement (aerobic or microaerophilic), nitrate reductase activity, susceptibility to pyrazinamide (60 micrograms/ml) and suscep... |
|
|
Subdivision of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for epidemiological purposes: a seven year study of the "Classical' and 'Asian' types of the human tubercle bacillus in South-East England.
J. Hyg. (Lond) 94(1) , 9-21, (1985) Human strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis were divided into the 'Classical' and 'Asian' types according to their sensitivity to thiophen-2-carboxylic acid hydrazide. The isolation of these two types in South-East England was studied during a seven-year peri... |