7-METHYLGUANOSINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE SODIUM SALT
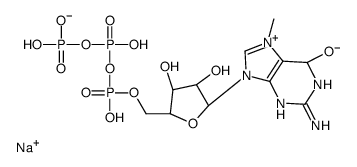
7-METHYLGUANOSINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE SODIUM SALT structure
|
Common Name | 7-METHYLGUANOSINE 5'-TRIPHOSPHATE SODIUM SALT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104809-18-9 | Molecular Weight | 561.20500 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H19N5NaO14P3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
BDNF stimulation of protein synthesis in cortical neurons requires the MAP kinase-interacting kinase MNK1.
J. Neurosci. 35(3) , 972-84, (2015) Although the MAP kinase-interacting kinases (MNKs) have been known for >15 years, their roles in the regulation of protein synthesis have remained obscure. Here, we explore the involvement of the MNKs in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-stimulated pro... |
|
|
Molecular mechanism of the dual activity of 4EGI-1: Dissociating eIF4G from eIF4E but stabilizing the binding of unphosphorylated 4E-BP1.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , E4036-45, (2015) The eIF4E-binding protein (4E-BP) is a phosphorylation-dependent regulator of protein synthesis. The nonphosphorylated or minimally phosphorylated form binds translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), preventing binding of eIF4G and the recruitment of the smal... |
|
|
c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylates DCP1a to control formation of P bodies.
J. Cell Biol. 194 , 581-96, (2011) Cytokines and stress-inducing stimuli signal through c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) using a diverse and only partially defined set of downstream effectors. In this paper, the decapping complex subunit DCP1a was identified as a novel JNK target. JNK phosphoryla... |
|
|
Impaired wound healing results from the dysfunction of the Akt/mTOR pathway in diabetic rats.
J. Dermatol. Sci. 79 , 241-51, (2015) Wound healing is impaired in diabetes mellitus. The underlying mechanism involved in this process is still unknown. The Akt/mTOR signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of diabetes.we investigated the role of the Akt/mTOR pathway in diabeti... |
|
|
Human cytomegalovirus TRS1 protein associates with the 7-methylguanosine mRNA cap and facilitates translation.
Proteomics 15 , 1983-94, (2015) Viruses rely on the host translation machinery for the synthesis of viral proteins. Human cells have evolved sensors that recognize viral RNAs and inhibit mRNA translation in order to limit virus replication. Understanding how viruses manipulate the host tran... |
|
|
Cul1 promotes melanoma cell proliferation by promoting DEPTOR degradation and enhancing cap-dependent translation.
Oncol. Rep. 35 , 1049-56, (2016) Cullin1 (Cul1) serves as a rigid scaffold in the SCF (Skp1/Cullin/Rbx1/F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex and has been found to be overexpressed in melanoma and to enhance melanoma cell proliferation by promoting G1-S phase transition. However, the un... |
|
|
Neural RNA-binding protein Musashi1 inhibits translation initiation by competing with eIF4G for PABP.
J. Cell Biol. 181 , 639-53, (2008) Musashi1 (Msi1) is an RNA-binding protein that is highly expressed in neural stem cells. We previously reported that Msi1 contributes to the maintenance of the immature state and self-renewal activity of neural stem cells through translational repression of m... |
|
|
The crystal structure of the PB2 cap-binding domain of influenza B virus reveals a novel cap recognition mechanism.
J. Biol. Chem. 290(14) , 9141-9, (2015) The influenza RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is a core enzyme required for both transcription and replication of the virus RNA genome, making it a potential drug target for the influenza virus. To detect the feature of cap-dependent transcription of influenza B... |
|
|
Specific regulation of mRNA cap methylation by the c-Myc and E2F1 transcription factors.
Oncogene 28 , 1169-75, (2009) Methylation of the mRNA 5' guanosine cap is essential for efficient gene expression. The 5' methyl cap binds to eIF4E, which is the first step in the recruitment of mRNA to the 40S ribosomal subunit. To investigate whether mRNA cap methylation is regulated in... |
|
|
A novel role for IGF-1R in p53-mediated apoptosis through translational modulation of the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop.
J. Cell Biol. 178 , 995-1007, (2007) Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) is important in cancer cell growth and survival and has been implicated in cancer pathophysiology and treatment. Here we report a novel function for IGF-1R in p53-dependent apoptotic response. We show that inhibi... |