D-Glucose-13C6,1,2,3,4,5,6,6-d7
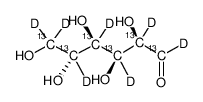
D-Glucose-13C6,1,2,3,4,5,6,6-d7 structure
|
Common Name | D-Glucose-13C6,1,2,3,4,5,6,6-d7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 201417-01-8 | Molecular Weight | 193.15500 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H5D7O6 | Melting Point | 150-152ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Metabolic network capacity of Escherichia coli for Krebs cycle-dependent proline hydroxylation.
Microb. Cell Fact. 14 , 108, (2015) Understanding the metabolism of the microbial host is essential for the development and optimization of whole-cell based biocatalytic processes, as it dictates production efficiency. This is especially true for redox biocatalysis where metabolically active ce... |
|
|
Antisense Oligonucleotide-mediated Suppression of Muscle Glycogen Synthase 1 Synthesis as an Approach for Substrate Reduction Therapy of Pompe Disease.
Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 3 , e206, (2014) Pompe disease is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency of acid α-glucosidase (GAA; EC 3.2.1.20) and the resultant progressive lysosomal accumulation of glycogen in skeletal and cardiac muscles. Enzyme replacement therapy using recombinant hum... |
|
|
Shigella reroutes host cell central metabolism to obtain high-flux nutrient supply for vigorous intracellular growth.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(27) , 9929-34, (2014) Shigella flexneri proliferate in infected human epithelial cells at exceptionally high rates. This vigorous growth has important consequences for rapid progression to life-threatening bloody diarrhea, but the underlying metabolic mechanisms remain poorly unde... |
|
|
Biosynthesis and genomic analysis of medium-chain hydrocarbon production by the endophytic fungal isolate Nigrograna mackinnonii E5202H.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99(8) , 3715-28, (2015) An endophytic fungus was isolated that produces a series of volatile natural products, including terpenes and odd chain polyenes. Phylogenetic analysis of the isolate using five loci suggests that it is closely related to Nigrograna mackinnonii CBS 674.75. Th... |
|
|
Solution NMR of MPS-1 reveals a random coil cytosolic domain structure.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e111035, (2014) Caenorhabditis elegans MPS1 is a single transmembrane helical auxiliary subunit that co-localizes with the voltage-gated potassium channel KVS1 in the nematode nervous system. MPS-1 shares high homology with KCNE (potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E m... |
|
|
Trauma/hemorrhagic shock instigates aberrant metabolic flux through glycolytic pathways, as revealed by preliminary (13)C-glucose labeling metabolomics.
J. Transl. Med. 13 , 253, (2015) Metabolic derangement is a key hallmark of major traumatic injury. The recent introduction of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics technologies in the field of trauma shed new light on metabolic aberrations in plasma that are triggered by trauma and hemorrhag... |
|
|
Pliable natural biocide: Jaburetox is an intrinsically disordered insecticidal and fungicidal polypeptide derived from jack bean urease.
FEBS J. 282(6) , 1043-64, (2015) Jaburetox is a polypeptide derived from jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) urease and toxic to a broad spectrum of insects, phytopathogenic filamentous fungi and yeasts of medical importance. The elucidation of the structural basis for the mode of action of Jab... |
|
|
Oligomeric Procyanidins Interfere with Glycolysis of Activated T Cells. A Novel Mechanism for Inhibition of T Cell Function.
Molecules 20 , 19014-26, (2015) Procyanidins, which are flavonoids that are found in a variety of plant species, reduce or prevent immune disorders, such as allergy and autoimmune diseases, through an unknown mechanism. In the present study, we investigated the effects of procyanidins on th... |
|
|
Structural and Dynamic Features of F-recruitment Site Driven Substrate Phosphorylation by ERK2.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 11127, (2015) The F-recruitment site (FRS) of active ERK2 binds F-site (Phe-x-Phe-Pro) sequences found downstream of the Ser/Thr phospho-acceptor on cellular substrates. Here we apply NMR methods to analyze the interaction between active ERK2 (ppERK2), and a 13-residue F-s... |
|
|
Interaction of S100A13 with C2 domain of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE).
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1844(9) , 1718-28, (2014) S100A13 is involved in several key biological functions like angiogenesis, tumor formation and cell apoptosis. It is a homodimeric protein that belongs to the S100 protein family. S100A13 is co-expressed with acidic fibroblast growth factor (FGF1) and interle... |