Cytochalasin B
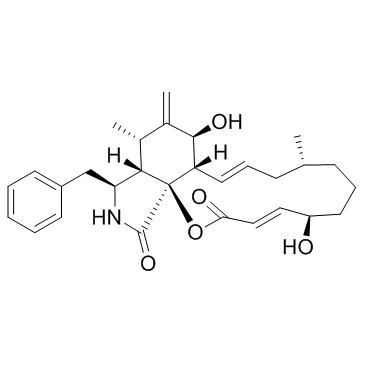
Cytochalasin B structure
|
Common Name | Cytochalasin B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 14930-96-2 | Molecular Weight | 479.608 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 740.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H37NO5 | Melting Point | 218-223ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 401.7±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Crystal structure of a glucose/H+ symporter and its mechanism of action.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(44) , 17862-7, (2013) Glucose transporters are required to bring glucose into cells, where it is an essential energy source and precursor in protein and lipid synthesis. These transporters are involved in important common diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Here, we report the c... |
|
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared and assayed 33 coumarin derivatives, and the theoretical pr... |
|
|
Discovery of the migrasome, an organelle mediating release of cytoplasmic contents during cell migration.
Cell Res. 25(1) , 24-38, (2015) Cells communicate with each other through secreting and releasing proteins and vesicles. Many cells can migrate. In this study, we report the discovery of migracytosis, a cell migration-dependent mechanism for releasing cellular contents, and migrasomes, the ... |
|
|
Golgicide A reveals essential roles for GBF1 in Golgi assembly and function.
Nat. Chem. Biol. , (2009) ADP ribosylation factor 1 (Arf1) plays a critical role in regulating secretory traffic and membrane transport within the Golgi of eukaryotic cells. Arf1 is activated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (ArfGEFs), which confer spatial and temporal specifici... |
|
|
Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Klyxum molle with inhibitory activity on superoxide generation and elastase release by neutrophils.
J. Nat. Prod. 76(9) , 1661-7, (2013) Eleven new eunicellin-based diterpenoids possessing a cladiellane skeleton with a C-2, C-9 ether bridge, klymollins I-S (1-11), have been isolated from the EtOAc extract of the soft coral Klyxum molle from Taiwan waters. The structures of compounds 1-11 were ... |
|
|
Identification of C-terminal phosphorylation sites of N-formyl peptide receptor-1 (FPR1) in human blood neutrophils.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(38) , 27042-58, (2013) Accumulation, activation, and control of neutrophils at inflammation sites is partly driven by N-formyl peptide chemoattractant receptors (FPRs). Occupancy of these G-protein-coupled receptors by formyl peptides has been shown to induce regulatory phosphoryla... |
|
|
Enlargement and multinucleation of u937 leukemia and MCF7 breast carcinoma cells by antineoplastic agents to enhance sensitivity to low frequency ultrasound and to DNA-directed anticancer agents.
Anticancer Res. 35(1) , 65-76, (2015) Cytochalasin B is a mycogenic toxin that preferentially damages malignant cells through multiple mechanisms. The microfilament-disrupting agent inhibits cytokinesis, producing enlarged and multinucleated neoplastic cells without enlarging or producing multinu... |
|
|
Small molecule regulators of autophagy identified by an image-based high-throughput screen.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104 , 19023-8, (2007) Autophagy is a lysosome-dependent cellular catabolic mechanism mediating the turnover of intracellular organelles and long-lived proteins. Reduction of autophagy activity has been shown to lead to the accumulation of misfolded proteins in neurons and may be i... |
|
|
Synthetic and pharmacological studies on new simplified analogues of the potent actin-targeting Jaspamide.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 6580-8, (2008) In the recent years, we focused our attention on the cyclodepsipeptide Jaspamide 1, an interesting marine metabolite, possessing a potent inhibitory activity against breast and prostate cancer, as a consequence of its ability to disrupt actin cytoskeleton dyn... |
|
|
Adeno-associated virus-targeted disruption of the CFTR gene in cloned ferrets.
J. Comp. Neurol. 118 , 1578-83, (2008) Somatic cell gene targeting combined with nuclear transfer cloning presents tremendous potential for the creation of new, large-animal models of human diseases. Mouse disease models often fail to reproduce human phenotypes, underscoring the need for the gener... |