SB 265610
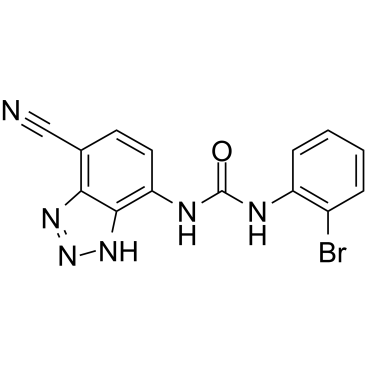
SB 265610 structure
|
Common Name | SB 265610 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 211096-49-0 | Molecular Weight | 357.16500 | |
| Density | 1.779 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H9BrN6O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 272.5ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Regulation of CXCR2 expression and function by a disintegrin and metalloprotease-17 (ADAM17).
J. Leukoc. Biol. 97(3) , 447-54, (2015) The chemokine receptor CXCR2 is expressed at high levels on circulating neutrophils and is critical for directing their migration to sites of inflammation. CXCR2 surface levels are rapidly modulated by 2 mechanisms-cell internalization and recycling upon liga... |
|
|
Discovery of Novel CXCR2 Inhibitors Using Ligand-Based Pharmacophore Models.
J. Chem. Inf. Model. 55 , 1720-38, (2015) The chemokine receptor CXCR2 is expressed on various immune cells and is essential for neutrophil recruitment and angiogenesis at sites of acute and chronic inflammation caused by tissue injury or infection. CXCR2 and its ligand, CXCL8, are implicated in a nu... |
|
|
Mesenchymal transition and dissemination of cancer cells is driven by myeloid-derived suppressor cells infiltrating the primary tumor.
PLoS Biol. 9 , e1001162, (2011) In order to metastasize, cancer cells need to acquire a motile phenotype. Previously, development of this phenotype was thought to rely on the acquisition of selected, random mutations and thus would occur late in cancer progression. However, recent studies s... |
|
|
SB225002 promotes mitotic catastrophe in chemo-sensitive and -resistant ovarian cancer cells independent of p53 status in vitro.
PLoS ONE 8(1) , e54572, (2013) Recent evidence indicates that CXCR2 signaling is crucial for cancer progression, and its antagonist SB225002 induces apoptosis in Wilms' tumor cells. Here, we investigated the effect of SB225002 on cell cycle progression and apoptosis induction in vitro, usi... |
|
|
Immune antibodies and helminth products drive CXCR2-dependent macrophage-myofibroblast crosstalk to promote intestinal repair.
PLoS Pathog. 11(3) , e1004778, (2015) Helminth parasites can cause considerable damage when migrating through host tissues, thus making rapid tissue repair imperative to prevent bleeding and bacterial dissemination particularly during enteric infection. However, how protective type 2 responses ta... |