1-Naphthalenol
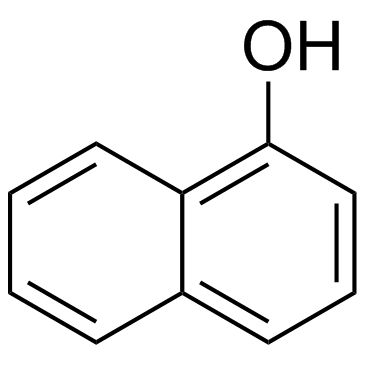
1-Naphthalenol structure
|
Common Name | 1-Naphthalenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90-15-3 | Molecular Weight | 144.170 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 288.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8O | Melting Point | 94-98ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 144.0±10.6 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Calcitonin controls bone formation by inhibiting the release of sphingosine 1-phosphate from osteoclasts.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5215, (2014) The hormone calcitonin (CT) is primarily known for its pharmacologic action as an inhibitor of bone resorption, yet CT-deficient mice display increased bone formation. These findings raised the question about the underlying cellular and molecular mechanism of... |
|
|
Rosmarinic acid attenuates hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 74 , 270-8, (2015) Rosmarinic acid (RosmA) demonstrates antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. We investigated the effect of RosmA on liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Rats were submitted to 60 min of ischemia plus saline or RosmA treatment (150 mg/kg BW intraperitoneal... |
|
|
Local administration of stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes stem cell recruitment and bone regeneration in a rat periodontal bone defect model.
Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 53 , 83-94, (2015) Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) recruits adult stem/progenitor cells via its specific receptor, C-X-C motif receptor 4 (CXCR4), to promote heart, kidney and tendon regeneration, but little is known about the effects of SDF-1 on bone regeneration in peri... |
|
|
Characterization of nitrogen-rich biomaterial-derived biochars and their sorption for aromatic compounds.
Environ. Pollut. 195 , 84-90, (2014) Biochars from nitrogen-rich biomaterials (i.e., α-amylase, chitin and zein) were produced at different temperatures (i.e. 170, 250, 350 and 450 °C) and characterized, and their sorption for phenanthrene, naphthalene and 1-naphthol was investigated. The organi... |
|
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the... |
|
|
Evaluation of the in vitro/in vivo potential of five berries (bilberry, blueberry, cranberry, elderberry, and raspberry ketones) commonly used as herbal supplements to inhibit uridine diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 72 , 13-9, (2014) In this study, we evaluated inhibitory potentials of popularly-consumed berries (bilberry, blueberry, cranberry, elderberry, and raspberry ketones) as herbal supplements on UGT1A1, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7 in vitro. We also investigated the potentia... |
|
|
Evaluation of thein vitro/in vivodrug interaction potential of BST204, a purified dry extract of ginseng, and its four bioactive ginsenosides through cytochrome P450 inhibition/induction and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase inhibition
Food Chem. Toxicol. 68 , 117-27, (2014) • BST204 is a purified dry extract of ginseng containing high amounts of Rh2 and Rg3. • BST204 had only weak inhibitory effects on nine CYPs and five UGTs. • It is unlikely that BST204 alter pharmacokinetics of drugs metabolized by CYPs/UGTs. |
|
|
Metabolic drug-drug interaction potential of macrolactin A and 7-O-succinyl macrolactin A assessed by evaluating cytochrome P450 inhibition and induction and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase inhibition in vitro.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(9) , 5036-46, (2014) Macrolactin A (MA) and 7-O-succinyl macrolactin A (SMA), polyene macrolides containing a 24-membered lactone ring, show antibiotic effects superior to those of teicoplanin against vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureu... |
|
|
Comparing immunocompetent and immunodeficient mice as animal models for bone tissue engineering.
Oral Dis. 21 , 583-92, (2015) To understand the differences and similarities between immunocompetent and immunodeficient mice as ectopic transplantation animal models for bone tissue engineering.Osteogenic cells from mouse leg bones were cultured, seeded on β-TCP granules, and transplante... |
|
|
3D cell culture and osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells plated onto jet-sprayed or electrospun micro-fiber scaffolds.
Biomed. Mater. 10 , 045019, (2015) A major limitation of the 2D culture systems is that they fail to recapitulate the in vivo 3D cellular microenvironment whereby cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions occur. In this paper, a biomaterial scaffold that mimics the structure o... |