dihydroferulic acid
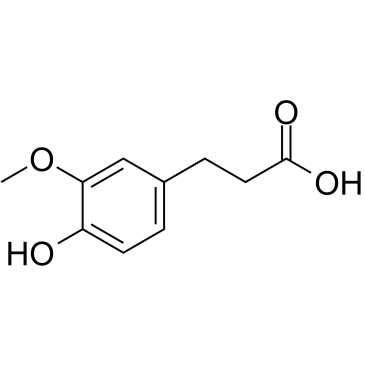
dihydroferulic acid structure
|
Common Name | dihydroferulic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1135-23-5 | Molecular Weight | 196.200 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 376.5±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O4 | Melting Point | 87-93 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 151.1±17.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Development of a targeted method for twenty-three metabolites related to polyphenol gut microbial metabolism in biological samples, using SPE and UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS.
Talanta 128 , 221-30, (2014) An increasing number of studies have concerned the profiling of polyphenol microbial metabolites, especially in urine or plasma, but only a few have regarded their accurate quantification. This study reports on a new ultra-performance liquid chromatography ta... |
|
|
Fate of microbial metabolites of dietary polyphenols in rats: is the brain their target destination?
ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6 , 1341-52, (2015) Different polyphenol compounds are ingested when consuming a serving of fruits rich in polyphenols, spanning from one-phenol hydroxybenzoic acid to more complex polymeric compounds. Only a minor quantity of the polyphenols (5-10%) is absorbed. The remainder r... |
|
|
Chronic administration of a microencapsulated probiotic enhances the bioavailability of orange juice flavanones in humans.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 84 , 206-14, (2015) Orange juice (OJ) flavanones are bioactive polyphenols that are absorbed principally in the large intestine. Ingestion of probiotics has been associated with favorable changes in the colonic microflora. The present study examined the acute and chronic effects... |
|
|
Polyphenol metabolites from colonic microbiota exert anti-inflammatory activity on different inflammation models.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 53(8) , 1044-54, (2009) The polyphenols in fruits and vegetables may be partly responsible for the health-promoting effects attributed to fruit and vegetable intake. Although their properties have been relatively well studied, the activity of their metabolites, produced after ingest... |