2,4′-dibromoacetophenone
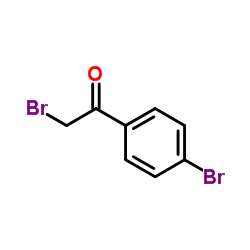
2,4′-dibromoacetophenone structure
|
Common Name | 2,4′-dibromoacetophenone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99-73-0 | Molecular Weight | 277.941 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 310.4±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6Br2O | Melting Point | 108-110 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 114.1±8.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Switching reversibility to irreversibility in glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors: clues for specific design of new compounds.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 4042-56, (2011) Development of kinase-targeted therapies for central nervous system (CNS) diseases is a great challenge. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) offers a great potential for severe CNS unmet diseases, being one of the inhibitors on clinical trials for different ta... |
|
|
Identification and characterisation of novel inhibitors on extrinsic tenase complex from Bungarus fasciatus (banded krait) venom.
Thromb. Haemost. 112(4) , 700-15, (2014) Snake venoms are excellent sources of pharmacologically active proteins and peptides, and hence are potential sources of leads for drug developments. It has been previously established that krait (Bungarus genus) venoms contain mainly neurotoxins. A screening... |
|
|
Effects of vipoxin and its components on HepG2 cells.
Toxicon 94 , 36-44, (2015) Snake venom Phospholipases A2 (svPLA2) are among the main toxic venom components with a great impact on different tissues and organs based on their catalytic specificity and a variety of pharmacological effects, whose mechanism is still under debate. The main... |
|
|
4-Bromophenacyl bromide specifically inhibits rhoptry secretion during Toxoplasma invasion.
PLoS ONE 4(12) , e8143, (2009) Toxoplasma gondii is a eukaryotic parasite of the phylum Apicomplexa that is able to infect a wide variety of host cells. During its active invasion process it secretes proteins from discrete secretory organelles: the micronemes, rhoptries and dense granules.... |
|
|
Rat atrial responses to Bothrops jararacussu (jararacuçu) snake venom.
Toxicology 323 , 109-24, (2014) Envenoming by the pitviper Bothrops jararacussu produces cardiovascular alterations, including coagulopathy, systemic hemorrhage, hypotension, circulatory shock and renal failure. In this work, we examined the activity of this venom in rat isolated right atri... |
|
|
Protection of rats against 3-butene-1,2-diol-induced hepatotoxicity and hypoglycemia by N-acetyl-l-cysteine.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 207(3) , 266-74, (2005) 3-Butene-1,2-diol (BDD), an allylic alcohol and major metabolite of 1,3-butadiene, has previously been shown to cause hepatotoxicity and hypoglycemia in male Sprague-Dawley rats, but the mechanisms of toxicity were unclear. In this study, rats were administer... |
|
|
Comparison of three derivatization reagents for the simultaneous determination of highly hydrophilic pyrimidine antitumor agents in human plasma by LC-MS/MS.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 893-894 , 49-56, (2012) A comparison of three derivatization reagents (dansyl chloride, diazomethane and p-bromophenacyl bromide) for the simultaneous quantitation of three anticancer chemicals (tegafur, 5-fluorouracil and gimeracil) and endogenous uracil in plasma using high perfor... |
|
|
A secretory PLA2 associated with tobacco hornworm hemocyte membrane preparations acts in cellular immune reactions.
Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 60(3) , 105-15, (2005) We report on a secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) associated with membrane-enriched fractions prepared from hemocytes of the tobacco hornworms, Manduca sexta. Virtually no PLA2 activity was detected in serum of immunologically naive or bacterially challenged ... |
|
|
Secretory phospholipase A2-alpha from Arabidopsis thaliana: functional parameters and substrate preference.
Chem. Phys. Lipids 150(2) , 156-66, (2007) The secretory phospholipase A2-alpha from Arabidopsis thaliana (AtsPLA2-alpha), being one of the first plant sPLA2s obtained in purified state, has been characterised with respect to substrate preference and optimum conditions of catalysis. The optima of pH, ... |
|
|
Production of medium-chain-length hydroxyalkanoic acids from Pseudomonas putida in pH stat.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 75 , 1047-1053, (2007) Pseudomonas putida GP01 cells that had accumulated medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA(MCL)) secreted 3-hydroxyoctanoate and 3-hydroxyhexanoate when incubated in alkaline buffers. The release of acids strongly decreased the pH resulting in less eff... |