4-Chloro-2-methylphenol
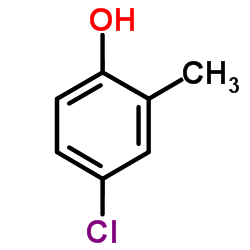
4-Chloro-2-methylphenol structure
|
Common Name | 4-Chloro-2-methylphenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1570-64-5 | Molecular Weight | 142.583 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 225.3±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7ClO | Melting Point | 43-46 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 90.1±21.8 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Chromatographic evaluation and QSAR optimization for benzoic acid analogues against carbonic anhydrase III.
J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 30 , 420-9, (2015) An HPLC-size exclusion method was developed as an assay method to evaluate the binding of tested compounds with carbonic anhydrase III (CAIII) enzyme. Inhibition of CAIII by a group of benzoic acid analogues was characterized by vacancy (negative) peak intens... |
|
|
Impact of induced fit on ligand binding to the androgen receptor: a multidimensional QSAR study to predict endocrine-disrupting effects of environmental chemicals.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 5666-74, (2005) We investigated the influence of induced fit of the androgen receptor binding pocket on free energies of ligand binding. On the basis of a novel alignment procedure using flexible docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and linear-interaction energy analysis... |
|
|
The effect of structure and a secondary carbon source on the microbial degradation of chlorophenoxy acids.
Chemosphere 79(11) , 1084-8, (2010) Pseudomonas putida, Aspergillus niger, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Sphingomonas herbicidovorans and Rhodococcus rhodochrous growing on glucose in a medium containing one of three chlorophenoxy acids at a concentration of 0.1 g L(-1) (clofibric... |
|
|
Etherolytic cleavage of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid and 4-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)butyric acid by species of Rhodococcus and Aureobacterium isolated from an alkaline environment.
J. Basic Microbiol. 38(4) , 257-267, (1998) Bacterial strains were isolated from the concrete rubble of a demolished herbicide production plant. The predominant feature of these strains was the etherolytic cleavage of 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid (DCPB)1) and 4-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)butyric ... |
|
|
Genotoxicity of ochratoxin A and structurally related compounds in Escherichia coli strains: studies on their mode of action.
IARC Sci. Publ. (115) , 261-6, (1991) Ochratoxin A, ochratoxin alpha (its major metabolite in rodents) and seven structurally related substances were assayed for SOS DNA repair inducing activity in Escherichia coli PQ37 strain. At a concentration range of 0.1-4 mM, ochratoxin A, chloroxine, 5-chl... |
|
|
Determination of the herbicide 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid and its main metabolite, 4-chloro-2-methylphenol in water and soil by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 923(1-2) , 75-85, (2001) A rapid and sensitive LC-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry method has been developed for the quantitation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) and 4-chloro-2-methylphenol in both water and soil samples. Soil samples were extracted in alkaline med... |
|
|
Functional properties of RYR1 mutations identified in Swedish patients with malignant hyperthermia and central core disease.
Anesth. Analg. 111(1) , 185-90, (2010) A diagnosis of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility by in vitro contraction testing can often only be performed at specialized laboratories far away from where patients live. Therefore, we have designed a protocol for genetic screening of the RYR1-cDNA and f... |
|
|
Pesticide by-products in the Rhône delta (Southern France). The case of 4-chloro-2-methylphenol and of its nitroderivative.
Chemosphere 74(4) , 599-604, (2009) A field monitoring campaign for pesticides and their transformation intermediates was carried out in the Rhône delta (Southern France). It was evidenced the following transformation sequence: MCPA-->4-chloro-2-methylphenol (CMP)-->4-chloro-2-methyl-6-nitrophe... |
|
|
Degradation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenol by an activated sludge isolate and its taxonomic description.
Biodegradation 6(2) , 83-92, (1995) The Gram-negative strain S1, isolated from activated sludge, metabolized 4-chloro-2-methylphenol by an inducible pathway via a modified ortho-cleavage route as indicated by a transiently secreted intermediate, identified as 2-methyl-4-carboxymethylenebut-2-en... |
|
|
Guinea pig maximization test: effect of type of Freund's complete adjuvant emulsion and of challenge site location.
Derm. Beruf Umwelt. 33(4) , 132-6, (1985) Guinea pig maximization tests (GPMT) with chlorocresol were performed to ascertain whether the sensitization rate was affected by minor changes in the Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA) emulsion used. Three types of emulsion were evaluated: the oil phase was mi... |