3,3',5'-triiodothyronine
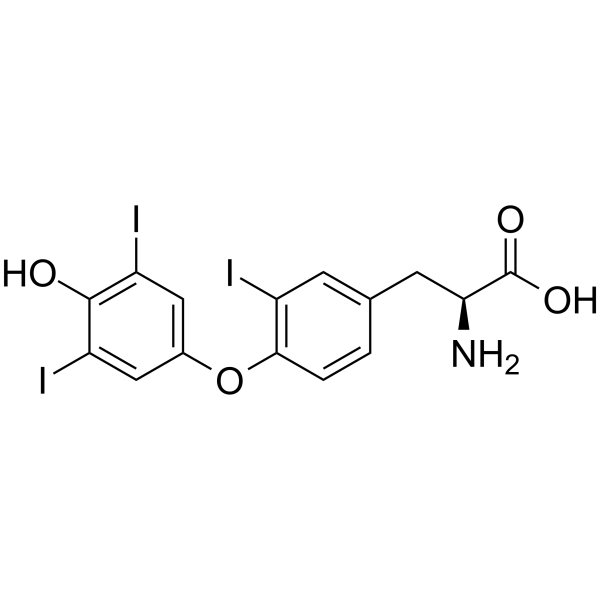
3,3',5'-triiodothyronine structure
|
Common Name | 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5817-39-0 | Molecular Weight | 650.974 | |
| Density | 2.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 534.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12I3NO4 | Melting Point | 234-238ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 277.1±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Postnatal overnutrition programs the thyroid hormone metabolism and function in adulthood.
J. Endocrinol. 226 , 219-26, (2015) Early overnutrition (EO) during lactation leads to obesity, leptin resistance and lower thyroid hormone (TH) levels during adulthood. To better understand the biological significance of this thyroid hypofunction, we studied the long-term effects of postnatal ... |
|
|
Heredity and lifestyle in the determination of between-subject variation in thyroid hormone levels in euthyroid men.
Eur. J. Endocrinol. 169(6) , 835-44, (2013) Variation in thyroid hormone (TH) concentrations between subjects is greater than in a single subject over a prolonged period of time, suggesting an individual set point for thyroid function. We have previously shown that TH levels within normal range are ass... |
|
|
Halogenated phenolic contaminants inhibit the in vitro activity of the thyroid-regulating deiodinases in human liver.
Toxicol. Sci. 124(2) , 339-47, (2011) Halogenated contaminants, particularly brominated flame retardants, disrupt circulating levels of thyroid hormones (THs), potentially affecting growth and development. Disruption may be mediated by impacts on deiodinase (DI) activity, which regulate the level... |
|
|
Energetic adaptations persist after bariatric surgery in severely obese adolescents.
Obesity (Silver Spring.) 23(3) , 591-601, (2015) Energetic adaptations induced by bariatric surgery have not been studied in adolescents or for extended periods postsurgery. Energetic, metabolic, and neuroendocrine responses to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery were investigated in extremely obese ado... |
|
|
Thyroid: biological actions of 'nonclassical' thyroid hormones.
J. Endocrinol. 221(2) , R1-12, (2014) Thyroid hormones (THs) are produced by the thyroid gland and converted in peripheral organs by deiodinases. THs regulate cell functions through two distinct mechanisms: genomic (nuclear) and nongenomic (non-nuclear). Many TH effects are mediated by the genomi... |
|
|
Glucagon-like peptide-1 stimulates type 3 iodothyronine deiodinase expression in a mouse insulinoma cell line
Life Sci. 115(1-2) , 22-8, (2014) Aims The pathophysiological roles of thyroid hormones in glucose metabolism remain uncertain. Type 3 iodothyronine deiodinase (D3) converts thyroxine (T4) and 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine (T3) to 3,3′,5′-triiodothyronine (rT3) and 3,3′-diiodothyronine (T2), respec... |
|
|
Harnessing the skin-thyroid connection for wound healing: a prospective controlled trial in guinea pigs.
Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 37(8) , 850-6, (2012) Different elements of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis have been found to be implicated in the normal physiology of the human skin. Their effects on wound healing and hair growth in rats have been described previously. There is close homology between t... |
|
|
Comparison and assessment of thyroid morphology and function in inhabitants of Lower Silesia before and after administration of a single dose of iodine-containing contrast agent during cardiac intervention procedure.
Endokrynol. Pol. 63(4) , 294-9, (2012) Inhabitants living in areas with endemic dietary iodine intake deficiency develop nodular goitre. The aim of our study was to evaluate thyroid morphology and function among adults residing in Lower Silesia and to assess the effect on the thyroid gland of an i... |
|
|
Deiodination in cancer growth: the role of type III deiodinase.
Minerva Endocrinol. 37(4) , 315-27, (2012) Thyroid hormone (TH) is a pleiotropic agent that has widespread biological functions, i.e., it controls cellular growth, tissue development and homeostasis and neoplastic transformation. Suitable TH levels are critical for the development of various types of ... |
|
|
Thyroid and bone.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 503(1) , 129-36, (2010) The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis plays a key role in skeletal development, acquisition of peak bone mass and regulation of adult bone turnover. Euthyroid status is essential for maintenance of optimal bone mineralization and strength. In population stu... |