Disopyramid phosphate
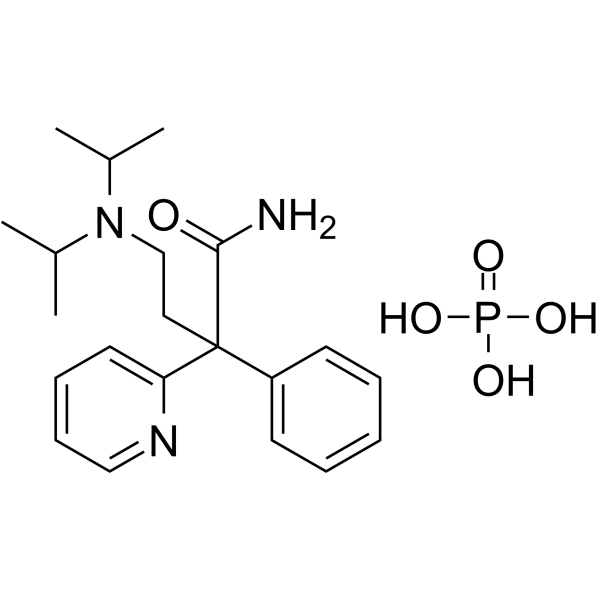
Disopyramid phosphate structure
|
Common Name | Disopyramid phosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22059-60-5 | Molecular Weight | 437.47000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 505.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H32N3O5P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 259.4ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A review of the effects of disopyramide phosphate on left ventricular function and the peripheral circulation.
Angiology 38(2 Pt 2) , 174-83, (1987) In the absence of preexistent myocardial dysfunction, the risk of producing cardiac decompensation in patients being treated with any of the conventional antiarrhythmic agents is low. The availability of disopyramide for clinical use in 1977 produced optimism... |
|
|
[Disopyramide phosphate: the electrophysiological mechanisms of its anti-arrhythmia action and its use in clinical practice].
Kardiologiia 25(5) , 114-8, (1985)
|
|
|
Disopyramide-induced hypoglycemia in a non-diabetic hemodialysis patient: a case report and review of the literature.
Clin. Nephrol. 76(5) , 401-6, (2011) Disopyramide, an antiarrhythmic drug, has been reported to cause hypoglycemia; however, its mechanism of action remains unclear. Pre-existing factors that increase the concentration of the drug in the blood increase the risk of hypoglycemia. Furthermore, othe... |
|
|
A primer of disopyramide treatment of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 54(6) , 483-92, (2012) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) occurs in 1 in 500 individuals. Treatment options for HCM differ from those administered in coronary disease, heart failure, and valvular disease patients that comprise the core of many cardiology practices. In this article, ... |
|
|
Monitoring disopyramide, lidocaine, and quinidine by micellar liquid chromatography.
J. AOAC Int. 94(2) , 537-42, (2011) A micellar liquid chromatography (MLC) method using a C18 column was developed to determine three antiarrhythmic drugs--disopyramide, lidocaine, and quinidine--that are most usually monitored in serum samples. After the application of an interpretative strate... |
|
|
Can pharmacologic gradient reduction decrease mortality in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 54(6) , 535-42, (2012) Pharmacologic therapy is the first line approach to relieve symptoms in obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. There are no randomized trials to evaluate their effect on prognosis. Gradient reduction by surgical septal myectomy is associated with excellent ... |
|
|
Torsades de Pointes induced by a combination of garenoxacin and disopyramide and other cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A polypeptide-4-influencing drugs during hypokalemia due to licorice.
Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 14(2) , 164-7, (2010) We report an 82-year-old man who developed ventricular tachycardia and Torsades de Pointes (TdP) after oral administration of garenoxacin, a novel quinolone antibiotic agent that differs from the third-generation quinolones, for pneumonia. He had hypokalemia ... |
|
|
[Drug treatment for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy].
Presse Med. 38(6) , 1001-4, (2009) Drug treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the first-line treatment, at the onset of clinical signs and symptoms. Beta-blockers are proposed for symptomatic patients with no gradient or with a gradient that appears only on exertion. Verapamil is the sta... |
|
|
Combined effect of disopyramide and erythromycin on ventricular repolarization in dogs with complete atrioventricular block.
Int. Heart J. 52(6) , 393-7, (2011) The combined effects of disopyramide (DP) and erythromycin (EM) on ventricular repolarization and the inciden-ces of ventricular premature contractions (VPCs) and torsades de pointes (TdP) were investigated in 12 anesthetized dogs with complete atrioventricul... |
|
|
Cardiac amyloidosis mimicking hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with obstruction: treatment with disopyramide.
Circulation 125(14) , 1821-4, (2012)
|