6-hydroxy Warfarin
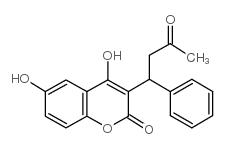
6-hydroxy Warfarin structure
|
Common Name | 6-hydroxy Warfarin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 17834-02-5 | Molecular Weight | 324.32700 | |
| Density | 1.384 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 540.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H16O5 | Melting Point | 119-120ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 197.7ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Investigation of two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography approaches for reversed phase resolution of warfarin and hydroxywarfarin isomers.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1363 , 200-6, (2014) Several offline and online 2D HPLC methods were investigated for the reversed phase resolution of a complex mixture of closely related warfarin and hydroxywarfarin isomers. By combining reversed phase achiral/chiral HPLC separation with UV-triggered fraction ... |
|
|
Hydroxywarfarin metabolites potently inhibit CYP2C9 metabolism of S-warfarin.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23(5) , 939-45, (2010) Coumadin (R/S-warfarin) anticoagulant therapy poses a risk to over 50 million Americans, in part due to interpersonal variation in drug metabolism. Consequently, it is important to understand how metabolic capacity is influenced among patients. Cytochrome P45... |
|
|
Metabolism of R- and S-warfarin by CYP2C19 into four hydroxywarfarins.
Drug Metab. Lett. 6(3) , 157-64, (2012) Coumadin (R/S-warfarin) is a highly efficacious and widely used anticoagulant; however, its highly variable metabolism remains an important contributor to uncertainties in therapeutic responses. Pharmacogenetic studies report conflicting findings on the clini... |
|
|
Warfarin is an effective modifier of multiple UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes: evaluation of its potential to alter the pharmacokinetics of zidovudine.
J. Pharm. Sci. 104(1) , 244-56, (2014) In this study, we aimed to determine the modulatory effects of warfarin (an extensively used anticoagulant drug) and its metabolites on UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) activity and to assess the potential of warfarin to alter the pharmacokinetics of zidovud... |
|
|
Analysis of R- and S-hydroxywarfarin glucuronidation catalyzed by human liver microsomes and recombinant UDP-glucuronosyltransferases.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 340(1) , 46-55, (2012) Coumadin (R-, S-warfarin) is a challenging drug to accurately dose, both initially and for maintenance, because of its narrow therapeutic range and wide interpatient variability and is typically administered as a racemic (Rac) mixture, which complicates the b... |
|
|
Development of a method for the analysis of warfarin and metabolites in plasma and urine.
Am. Clin. Lab. 14(7) , 20-1, (1995)
|
|
|
Impaired (S)-warfarin metabolism catalysed by the R144C allelic variant of CYP2C9.
Pharmacogenetics 4(1) , 39-42, (1994)
|
|
|
Identification of hydroxywarfarin binding site in human UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1a10: phenylalanine90 is crucial for the glucuronidation of 6- and 7-hydroxywarfarin but not 8-hydroxywarfarin.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 36(11) , 2211-8, (2008) Recent studies show that the extrahepatic human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A10 is capable of phase II glucuronidation of several major cytochrome P450 metabolites of warfarin (i.e., 6-, 7-, and 8-hydroxywarfarin). This study expands on this finding by ... |
|
|
Hydroxylation of warfarin by human cDNA-expressed cytochrome P-450: a role for P-4502C9 in the etiology of (S)-warfarin-drug interactions.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 5(1) , 54-9, (1992) Previous kinetic studies have identified a high-affinity (S)-warfarin 7-hydroxylase present in human liver microsomes which appears to be responsible for the termination of warfarin's biological activity. Inhibition of the formation of (S)-7-hydroxywarfarin, ... |
|
|
The population pharmacokinetics of R- and S-warfarin: effect of genetic and clinical factors.
Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 73(1) , 66-76, (2012) Warfarin is a drug with a narrow therapeutic index and large interindividual variability in daily dosing requirements. Patients commencing warfarin treatment are at risk of bleeding due to excessive anticoagulation caused by overdosing. The interindividual va... |