Vidarabine
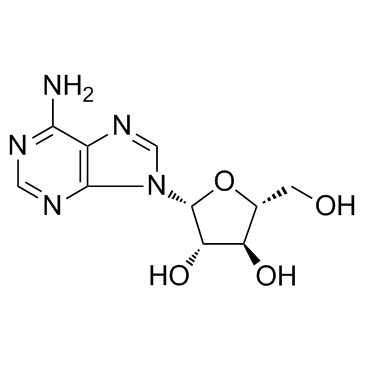
Vidarabine structure
|
Common Name | Vidarabine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5536-17-4 | Molecular Weight | 267.241 | |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 676.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O4 | Melting Point | 260-265ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 362.8±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Attenuation of vesicular stomatitis virus infection of brain using antiviral drugs and an adeno-associated virus-interferon vector.
Virology 475 , 1-14, (2014) Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) shows promise as a vaccine-vector and oncolytic virus. However, reports of neurotoxicity of VSV remain a concern. We compared 12 antiviral compounds to control infection of VSV-CT9-M51 and VSV-rp30 using murine and human brain... |
|
|
Treatment practice in the elderly patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia-analysis of the combined SEER and Medicare database.
Ann. Hematol. 93(8) , 1335-44, (2014) The median age at diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is 72, but patients enrolled in randomized trials are often a decade younger. Therapy selection and outcomes in the older, comorbid population are less understood. We evaluated treatment patter... |
|
|
Poor efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation.
Am. J. Hematol. 89(12) , E239-43, (2014) This phase II trial evaluated efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP for up to 8 courses in Richter transformation (RT) and up to 6 courses in CLL plus autoimmune cytopenia (AIC) or high-risk (HR) features. HR was defined as fludarabine-refractoriness or early r... |
|
|
Targeting the proliferative and chemoresistant compartment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by inhibiting survivin protein.
Leukemia 28(10) , 1993-2004, (2014) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells located in proliferation centers are constantly stimulated by accessory cells, which provide them with survival and proliferative signals and mediate chemotherapy resistance. Herein, we designed an experimental strateg... |
|
|
The investigational agent MLN2238 induces apoptosis and is cytotoxic to CLL cells in vitro, as a single agent and in combination with other drugs.
Br. J. Haematol. 165(1) , 78-88, (2014) Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is the most common haematological malignancy in the U.S. The course of the disease has been shown to be negatively impacted by increased levels of BCL2. Strategies to downregulate BCL2 and shift the balance towards cellular... |
|
|
Reduced intensity conditioning and oral care measures prevent oral mucositis and reduces days of hospitalization in allogeneic stem cell transplantation recipients.
Support Care Cancer 22(8) , 2133-40, (2014) Oral mucositis (OM) is a side effect of intensive chemotherapy and radiation and has been reported to affect 75-100% of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) recipients. The purpose of this study was to compare the incidence of OM in patients conditi... |