Dacarbazine
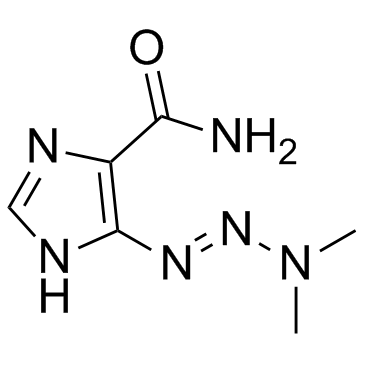
Dacarbazine structure
|
Common Name | Dacarbazine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4342-03-4 | Molecular Weight | 182.183 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 456.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N6O | Melting Point | 199-205°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 229.7±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Direct chemosensitivity monitoring ex vivo on undissociated melanoma tumor tissue by impedance spectroscopy.
Cancer Res. 74(22) , 6408-18, (2014) Stage III/IV melanoma remains incurable in most cases due to chemotherapeutic resistance. Thus, predicting and monitoring chemotherapeutic responses in this setting offer great interest. To overcome limitations of existing assays in evaluating the chemosensit... |
|
|
Dacarbazine as a minor groove binder of DNA: Spectroscopic, biophysical and molecular docking studies.
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 79 , 193-200, (2015) A detailed investigation on the mode of action and binding mechanism of a potent anticancer drug, 5-(3,3-dimethyl-1-triazeno)-imidazole-4-carboxamide (DCR) with calf thymus DNA (ctDNA) was carried out. UV-vis and fluorescence spectrophotometry suggested the f... |
|
|
A pro-apoptotic function of iASPP by stabilizing p300 and CBP through inhibition of BRMS1 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity.
Cell Death Dis. 6 , e1634, (2015) The p53 family and its cofactors are potent inducers of apoptosis and form a barrier to cancer. Here, we investigated the impact of the supposedly inhibitory member of the apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53, iASPP, on the activity of the p53 homolog TAp73, ... |
|
|
[Effectiveness and toxicity of MOPP, ABVD, BEACOPP chemotherapy in first-diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma with a poor prognosis].
Vopr. Onkol. 59(2) , 59-65, (2013) In a retrospective study during the primary mode MOPP to primary patients LH II/IVAB stages with a poor prognosis rate of CR, 5--and 10-year DFS, OS was 69%, 71% and 68%, 74% and 64%, ABVD--76%, 78%, 83% and 68%, BEACOPP-baseline--73%, 97%, 85% and 82%, respe... |
|
|
[Treatment of advanced Hodgkin lymphoma].
Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 138(23) , 1212-4, (2013)
|
|
|
A human monoclonal antibody targeting the stem cell factor receptor (c-Kit) blocks tumor cell signaling and inhibits tumor growth.
Cancer Biol. Ther. 15(9) , 1208-18, (2014) Stem cell factor receptor (c-Kit) exerts multiple biological effects on target cells upon binding its ligand stem cell factor (SCF). Aberrant activation of c-Kit results in dysregulated signaling and is implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous cancers. The ... |
|
|
A FAK scaffold inhibitor disrupts FAK and VEGFR-3 signaling and blocks melanoma growth by targeting both tumor and endothelial cells.
Cell Cycle 13(16) , 2542-53, (2014) Melanoma has the highest mortality rate of all skin cancers and a major cause of treatment failure is drug resistance. Tumors heterogeneity requires novel therapeutic strategies and new drugs targeting multiple pathways. One of the new approaches is targeting... |
|
|
Etoposide and temozolomide in combination for the treatment of progressive small-cell lung cancer central nervous system metastases: two cases.
Tumori 99(2) , e73-6, (2013) Progression of central nervous system (CNS) metastases from small cell lung cancer (SCLC) after radiation therapy is associated with a poor prognosis.We present two cases of patients with progressive CNS metastases from SCLC treated with oral temozolomide and... |
|
|
Durable response of intracranial cellular hemangioma to bevacizumab and temozolomide.
J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 11(6) , 682-6, (2013) Cellular hemangioma is a subtype of hemangioma that is associated with cellular immaturity and the potential for recurrence. Intracranial location of these lesions is extremely rare, and definitive treatment often requires radical neurosurgical resection. The... |
|
|
Leptomeningeal and intramedullary metastases of glioblastoma multiforme in a patient reoperated during adjuvant radiochemotherapy.
World J. Surg. Oncol. 11 , 55, (2013) Despite huge advances in medicine, glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) remains a highly lethal, fast-growing tumour that cannot be cured by currently available therapies. However, extracranial and extraneural dissemination of GBM is extremely rare, but is being rec... |