Vitamin A
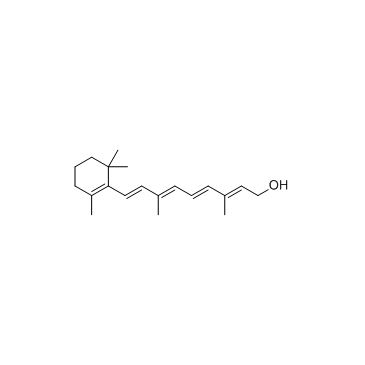
Vitamin A structure
|
Common Name | Vitamin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68-26-8 | Molecular Weight | 286.452 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 421.2±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O | Melting Point | 61-63 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 147.3±16.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Selective lentiviral gene delivery to CD133-expressing human glioblastoma stem cells.
PLoS ONE 9(12) , e116114, (2014) Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a deadly primary brain malignancy. Glioblastoma stem cells (GSC), which have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into tumor lineages, are believed to cause tumor recurrence due to their resistance to current therapies.... |
|
|
Impact of vitamin C on the cardiometabolic and inflammatory profiles of mice lacking a functional Werner syndrome protein helicase.
Exp. Gerontol. 72 , 192-203, (2015) Werner syndrome (WS) is a premature aging disorder caused by mutations in a DNA helicase/exonuclease. Mice lacking the helicase domain of this protein exhibit metabolic abnormalities that are reversed by vitamin C. In this study, we used a targeted metabolomi... |
|
|
Effect of concentrate feeder design on performance, eating and animal behavior, welfare, ruminal health, and carcass quality in Holstein bulls fed high-concentrate diets.
J. Anim. Sci. 93 , 3018-33, (2015) A total of 240 Holstein bulls (121 ± 2.0 kg initial BW; 99 ± 1.0 d of age), from 2 consecutive fattening cycles, were randomly allocated in 1 of 6 pens and assigned to 1 of the 3 treatments consisting of different concentrate feeder designs: a control feeder ... |
|
|
Akt‑mediated phosphorylation of Oct4 is associated with the proliferation of stem‑like cancer cells.
Oncol. Rep. 33(4) , 1621-9, (2015) Oct4 protein encoded by POU5F1 plays a pivotal role in maintaining the self‑renewal of pluripotent stem cells; however, its presence in cancer cells remains controversial. In the present study, we provided evidence that the transcripts of authentic OCT4 gene ... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
The Japanese toxicogenomics project: application of toxicogenomics.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 54 , 218-27, (2010) Biotechnology advances have provided novel methods for the risk assessment of chemicals. The application of microarray technologies to toxicology, known as toxicogenomics, is becoming an accepted approach for identifying chemicals with potential safety proble... |
|
|
QSPR modeling of octanol/water partition coefficient for vitamins by optimal descriptors calculated with SMILES.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43 , 714-40, (2008) Simplified molecular input line entry system (SMILES) has been utilized in constructing quantitative structure-property relationships (QSPR) for octanol/water partition coefficient of vitamins and organic compounds of different classes by optimal descriptors.... |
|
|
Use of miRNA response sequences to block off-target replication and increase the safety of an unattenuated, glioblastoma-targeted oncolytic HSV.
Mol. Ther. 23(1) , 99-107, (2015) Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is an aggressive brain cancer for which there is no effective treatment. Oncolytic HSV vectors (oHSVs) are attenuated lytic viruses that have shown promise in the treatment of human GBM models in animals, but their efficacy in ea... |
|
|
Capillary electromigration techniques as tools for assessing the status of vitamins A, C and E in patients with cystic fibrosis.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 45-53, (2014) The purpose of this work is the evaluation of the nutritional status of patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), based on the level of vitamin C in urine and vitamins A and E in serum, using the fast, selective and fully automated micellar electrokinetic capillary... |