trans-4-Carboxy-L-proline
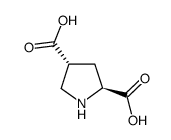
trans-4-Carboxy-L-proline structure
|
Common Name | trans-4-Carboxy-L-proline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64769-66-0 | Molecular Weight | 159.14000 | |
| Density | 1.456 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 355.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 168.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Evidence for a role of GABA- and glutamate-gated chloride channels in olfactory memory.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 103(1) , 69-75, (2012) In the honeybee, we investigated the role of transmissions mediated by GABA-gated chloride channels and glutamate-gated chloride channels (GluCls) of the mushroom bodies (MBs) on olfactory learning using a single-trial olfactory conditioning paradigm. The GAB... |
|
|
Substituted pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid amides as potent dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16(12) , 3268-72, (2006) A series of substituted pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid amides were synthesized as potential antidiabetic agents, and many of them showed good in vitro DPP-IV inhibition (IC50 = 2-250 nM) with selectivity over DPP-II, DPP8, and FAP enzymes. Selected compoun... |
|
|
The effects of local perfusion of DAMGO on extracellular GABA and glutamate concentrations in the rostral ventromedial medulla.
J. Neurochem. 104(3) , 806-17, (2008) Electrophysiological data suggest an involvement of rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM) GABA and glutamate (GLU) neurons in morphine analgesia. Direct evidence that extracellular concentrations of GABA or GLU are altered in response to mu opioid receptor (MOP-... |
|
|
Effects of theanine, r-glutamylethylamide, on neurotransmitter release and its relationship with glutamic acid neurotransmission.
Nutr. Neurosci. 8(4) , 219-26, (2005) t Theanine, r-glutamylethylamide, is one of the major amino acid components in green tea and many researchers have compared theanine's effects with glutamic acid because the chemical structure is similar. In the previous study, we demonstrated that theanine c... |
|
|
Dissociation between hippocampal neuronal loss, astroglial and microglial reactivity after pharmacologically induced reverse glutamate transport.
Neurochem. Int. 49(7) , 691-7, (2006) The inflammatory central nervous system response that involves activated microglia and reactive astrocytes may both heal and harm neurons, as inflammatory mediators lead to neuroprotection or excitation at one dose but to injury at a different concentration. ... |
|
|
Cerebral neurons of transgenic ALS mice are vulnerable to glutamate release stimulation but not to increased extracellular glutamate due to transport blockade.
Exp. Neurol. 199(2) , 281-90, (2006) Mechanisms of motor neuron loss in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are unknown, but it has been postulated that excitotoxicity due to excessive glutamatergic neurotransmission by decreased efficiency of glutamate transport may be involved in both familial... |
|
|
Region-specific neuroprotective effect of ZM 241385 towards glutamate uptake inhibition in cultured neurons.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 617(1-3) , 28-32, (2009) Active uptake by neurons and glial cells is the main mechanism for maintaining extracellular glutamate at low, non-toxic concentrations. Adenosine A(2A) receptors regulate extracellular glutamate levels by acting on both the release and the uptake of glutamat... |
|
|
In vivo modulation of alpha7 nicotinic receptors on striatal glutamate release induced by anatoxin-A.
Neurochem. Int. 56(6-7) , 850-5, (2010) In vitro studies suggest that alpha7 nicotinic receptors located on striatal glutamatergic terminals stimulate the release of glutamate which in turn acts at ionotropic glutamate receptors on dopaminergic terminals to increase dopamine release. However, this ... |
|
|
Glutamatergic and GABAergic effects of fipronil on olfactory learning and memory in the honeybee.
Invert. Neurosci. 9(2) , 91-100, (2009) We investigated here the role of transmissions mediated by GABA and glutamate-gated chloride channels (GluCls) in olfactory learning and memory in honeybees, both of these channels being a target for fipronil. To do so, we combined olfactory conditioning with... |
|
|
Unexpected inhibitory regulation of glutamate release from rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals by presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine-2A receptors.
J. Neurosci. Res. 84(7) , 1528-42, (2006) Presynaptic 5-HT(2A) receptor modulation of glutamate release from rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals (synaptosomes) was investigated by using the 5-HT(2A/2C) receptor agonist (+/-)-1-[2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl]-2-aminopropane (DOI). DOI potently inhibited ... |