2,6-Xylenol
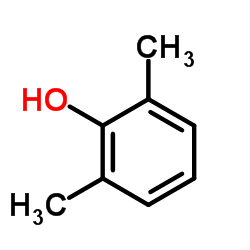
2,6-Xylenol structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-Xylenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 576-26-1 | Molecular Weight | 122.164 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 201.1±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O | Melting Point | 43-45 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 78.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Increased tolerance to salt stress in OPDA-deficient rice ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE mutants is linked to an increased ROS-scavenging activity.
J. Exp. Bot. 66 , 3339-52, (2015) Salinity stress represents a global constraint for rice, the most important staple food worldwide. Therefore the role of the central stress signal jasmonate for the salt response was analysed in rice comparing the responses to salt stress for two jasmonic aci... |
|
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the... |
|
|
Cellular apoptosis and cytotoxicity of phenolic compounds: a quantitative structure-activity relationship study.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 7234-42, (2005) In this comprehensive study on the caspase-mediated apoptosis-inducing effect of 51 substituted phenols in a murine leukemia cell line (L1210), we determined the concentrations needed to induce caspase activity by 50% (I50) and utilized these data to develop ... |
|
|
An improved model for the binding of lidocaine and structurally related local anaesthetics to fast-inactivated voltage-operated sodium channels, showing evidence of cooperativity.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 141(1) , 47-54, (2004) 1. The interaction of lidocaine-like local anaesthetics with voltage-operated sodium channels is traditionally assumed to be characterized by tighter binding of the drugs to depolarized channels. As inactivated and drug-bound channels are both unavailable on ... |
|
|
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of human erythrocyte isozymes I and II with a series of antioxidant phenols.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 3207-11, (2009) The inhibition of two human cytosolic carbonic anhydrase (hCA, EC 4.2.1.1) isozymes I and II, with a series of phenol derivatives was investigated by using the esterase assay, with 4-nitrophenyl acetate as substrate. 2,6-Dimethylphenol, 2,6-diisopropylphenol ... |
|
|
Structure-based shape pharmacophore modeling for the discovery of novel anesthetic compounds.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 5133-8, (2009) Current anesthetics, especially the inhaled ones, have troublesome side effects and may be associated with durable changes in cognition. It is therefore highly desirable to develop novel chemical entities that reduce these effects while preserving or enhancin... |
|
|
Acute toxicity of cresols, xylenols, and trimethylphenols to Daphnia magna Straus 1820.
Sci. Total Environ. 76(1) , 79-83, (1988) Twenty-four-hour IC50 values (50% immobilization concentration) for phenol, o-cresol, m-cresol, p-cresol, six xylenols, and three trimethylphenols were determined for Daphnia magna under static conditions. Our results show that cresols are more toxic than phe... |
|
|
Tropospheric multiphase chemistry of 2,5- and 2,6-dimethylphenols: determination of the mass accommodation coefficients and the Henry's law constants.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8(14) , 1714-23, (2006) The uptake of 2,5-dimethylphenol and 2,6-dimethylphenol on aqueous surfaces was measured between 279 and 293 K, using the wetted-wall flow tube technique coupled with UV absorption spectroscopic detection. For both compounds, the uptake coefficients gamma wer... |
|
|
Block of voltage-operated sodium channels by 2,6-dimethylphenol, a structural analogue of lidocaine's aromatic tail.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 137(2) , 285-93, (2002) 1. The structural features that determine the state-dependent interaction of local anaesthetics with voltage-operated sodium channels are still a matter of debate. We have studied the blockade of sodium channels by 2,6-dimethylphenol, a phenol derivative whic... |
|
|
[Occurrence of phenolic compounds in the dust of swine stalls and henhouses].
Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. B. 179(5) , 431-9, (1984) Dust-borne phenols and indols were extracted by ethanol from the sedimentation dust of two pig houses (finishing pigs on half slatted floor resp. piglets on deep litter) and a hen house (3-stage battery cages) and analysed by gas chromatography. In the dust o... |