Triclosan
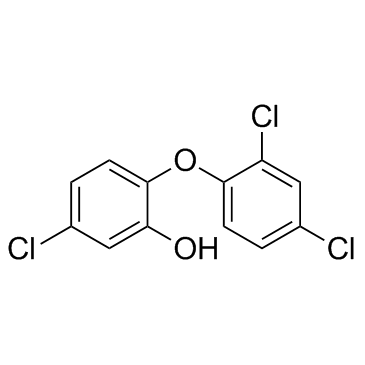
Triclosan structure
|
Common Name | Triclosan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3380-34-5 | Molecular Weight | 289.542 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 344.6±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H7Cl3O2 | Melting Point | 56-60 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 162.2±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Determination of plaque viability following a single brushing with commercial toothpastes.
J. Clin. Dent. 24(1) , 20-4, (2013) The purpose of this study was to determine the viability of dental plaque at 12 hours following brushing with Colgate Great Regular Flavor (0.83% MFP), Crest Pro-Health (0.454% SnF), and Colgate Total Clean Mint Toothpaste (0.3% triclosan/ copolymer/0.22% NaF... |
|
|
Antibacterial activity of fluoride compounds and herbal toothpastes on Streptococcus mutans: an in vitro study.
Aust. Dent. J. 60 , 368-74, (2015) Streptococcus mutans is an important bacterial species implicated in dental caries. This laboratory study compared the antimicrobial activity of a number of fluoride containing and herbal dentifrices and their components against S. mutans.An agar diffusion me... |
|
|
RamA confers multidrug resistance in Salmonella enterica via increased expression of acrB, which is inhibited by chlorpromazine.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 , 3604-11, (2008) Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344, in which efflux pump genes (acrB, acrD, acrF, tolC) or regulatory genes thereof (marA, soxS, ramA) were inactivated, was grown in the presence of 240 antimicrobial and nonantimicrobial agents in the Biolog Pheno... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Atmospheric pressure gas chromatography-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry (APGC-ToF-MS) for the determination of regulated and emerging contaminants in aqueous samples after stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE).
Anal. Chim. Acta 851 , 1-13, (2014) This work presents the development, optimization and validation of a multi-residue method for the simultaneous determination of 102 contaminants, including fragrances, UV filters, repellents, endocrine disruptors, biocides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (P... |
|
|
Multiresidue method for the determination of pharmacologically active substances in egg and honey using a continuous solid-phase extraction system and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Food Chem. 178 , 63-9, (2015) A sensitive, selective, efficient gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of 22 pharmacologically active substances (antibacterials, nonsteroidal antiinflammatories, antiseptics, antiepileptics, lipid regulators, β-block... |
|
|
Surfactants, aromatic and isoprenoid compounds, and fatty acid biosynthesis inhibitors suppress Staphylococcus aureus production of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 , 1898-906, (2009) Menstrual toxic shock syndrome is a rare but potentially life-threatening illness manifest through the actions of Staphylococcus aureus toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1). Previous studies have shown that tampon additives can influence staphylococcal TSST-... |
|
|
Phase II metabolism in human skin: skin explants show full coverage for glucuronidation, sulfation, N-acetylation, catechol methylation, and glutathione conjugation.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43(1) , 126-39, (2014) Although skin is the largest organ of the human body, cutaneous drug metabolism is often overlooked, and existing experimental models are insufficiently validated. This proof-of-concept study investigated phase II biotransformation of 11 test substrates in fr... |
|
|
Aldehyde oxidase activity in fresh human skin.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(12) , 2049-57, (2014) Human aldehyde oxidase (AO) is a molybdoflavoenzyme that commonly oxidizes azaheterocycles in therapeutic drugs. Although high metabolic clearance by AO resulted in several drug failures, existing in vitro-in vivo correlations are often poor and the extrahepa... |
|
|
Monitoring and removal of residual phthalate esters and pharmaceuticals in the drinking water of Kaohsiung City, Taiwan.
J. Hazard. Mater. 277 , 53-61, (2014) This study monitored the occurrence and removal efficiencies of 8 phthalate esters (PAEs) and 13 pharmaceuticals present in the drinking water of Kaohsiung City, Taiwan. The simultaneous electrocoagulation and electrofiltration (EC/EF) process was used to rem... |