N-Nitrosodimethylamine
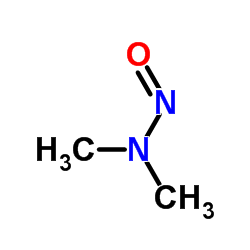
N-Nitrosodimethylamine structure
|
Common Name | N-Nitrosodimethylamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 62-75-9 | Molecular Weight | 74.082 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 152.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H6N2O | Melting Point | 50ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 36.1±18.7 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
[Effect of cordyceps polysaccharide on lipid peroxidation of rats with dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38(3) , 391-6, (2013) To observe the pharmacological effect of Cordyceps polysaccharide on dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced liver fibrosis in rats.DMN rat liver fibrosis model was established and divided into the normal group (N, n = 6), the model group (M, n = 11), the Cordyceps... |
|
|
Relationship between organic precursors and N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) formation in tropical water sources.
J. Water Health 12(4) , 736-46, (2014) The presence of organic compounds in water sources is one of the concerns in water treatment. They are potential precursors of disinfection byproducts (DBPs) and thus induce health problems in humans. Among the emerging DBPs, carcinogenic compound N-nitrosodi... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Safety evaluation of standardized allergen extract of Japanese cedar pollen for sublingual immunotherapy.
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 71(3) , 529-40, (2015) Japanese cedar (JC) pollinosis is caused by Japanese cedar pollen (JCP) and most common seasonal allergic disease in Japan. Subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) with allergen extract of JCP (JCP-allergen extract) is well established for JC pollinosis treatment w... |
|
|
A salting out-acetonitrile homogeneous extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of thirteen N-nitrosamines in skin care cosmetics.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1422 , 82-8, (2015) A sensitive gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method was established for the simultaneous determination of thirteen N-nitrosamines (NAs) in skin care cosmetics. The cosmetics samples were firstly dispersed by water and subsequently extracted and purified u... |
|
|
The roles of tertiary amine structure, background organic matter and chloramine species on NDMA formation.
Water Res. 47(2) , 945-53, (2013) N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), a probable human carcinogen, is a disinfection by-product that has been detected in chloraminated and chlorinated drinking waters and wastewaters. Formation mechanisms and precursors of NDMA are still not well understood. The ma... |
|
|
Increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in zucker diabetic rat liver and brain.
Cell Physiol. Biochem. 35(3) , 1241-51, (2015) The Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF, FA/FA) rat is a genetic model of type 2 diabetes, characterized by insulin resistance with progressive metabolic syndrome. We have previously demonstrated mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in the heart, kidneys and... |
|
|
Cross-platform toxicogenomics for the prediction of non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogenesis in rat.
PLoS ONE 9(5) , e97640, (2014) In the area of omics profiling in toxicology, i.e. toxicogenomics, characteristic molecular profiles have previously been incorporated into prediction models for early assessment of a carcinogenic potential and mechanism-based classification of compounds. Tra... |
|
|
Whey-hydrolyzed peptide-enriched immunomodulating diet prevents progression of liver cirrhosis in rats.
Nutrition 30(10) , 1195-207, (2014) Liver fibrosis and subsequent cirrhosis is a major cause of death worldwide, but few effective antifibrotic therapies are reported. Whey-hydrolyzed peptide (WHP), a major peptide component of bovine milk, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in experimental model... |