| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
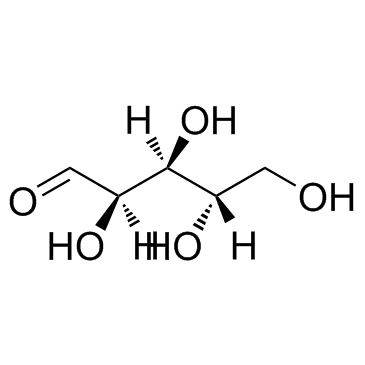 |
L-(+)-Arabinose
CAS:5328-37-0 |
|
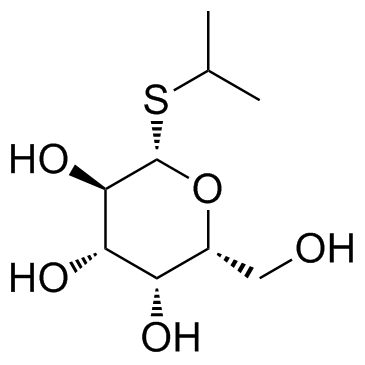 |
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside
CAS:367-93-1 |
|
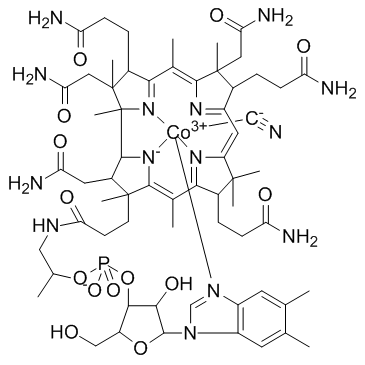 |
Vitamin B12
CAS:68-19-9 |
|
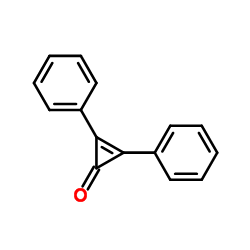 |
DPC
CAS:886-38-4 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
 |
Amphotericin B
CAS:1397-89-3 |