| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
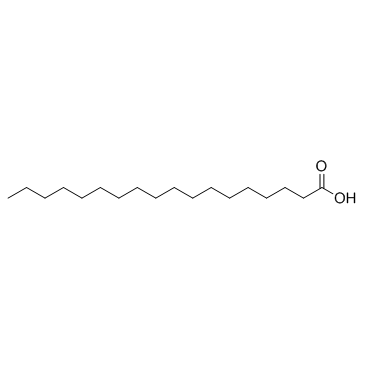 |
stearic acid
CAS:57-11-4 |
|
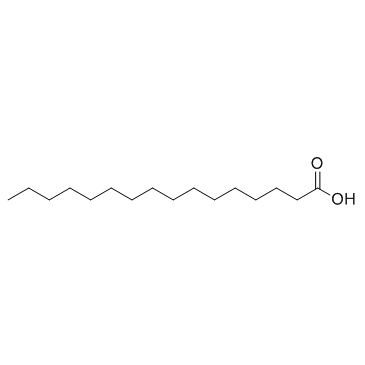 |
Palmitic acid
CAS:57-10-3 |
|
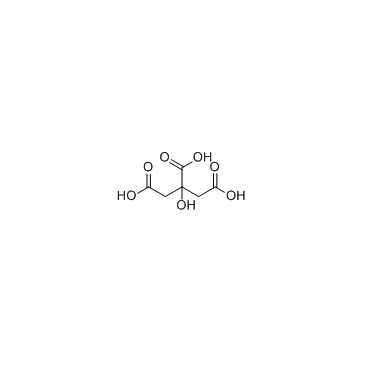 |
Citric Acid
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
 |
Fructose
CAS:57-48-7 |
|
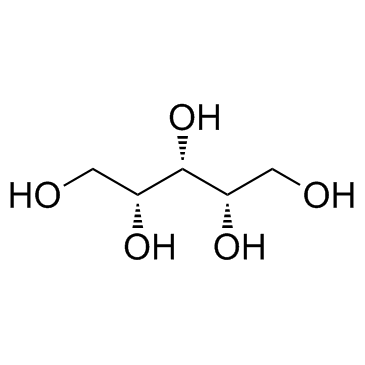 |
Xylitol
CAS:87-99-0 |
|
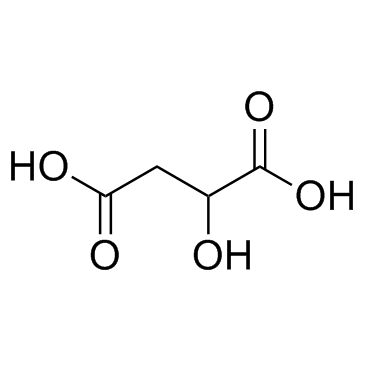 |
(±)-Malic Acid
CAS:6915-15-7 |
|
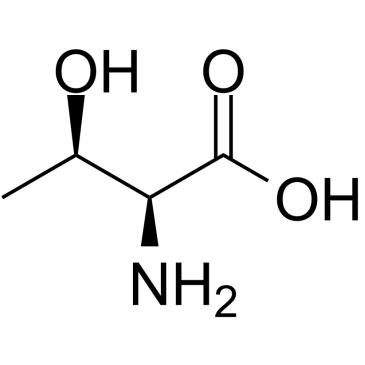 |
L-Threonine
CAS:72-19-5 |
|
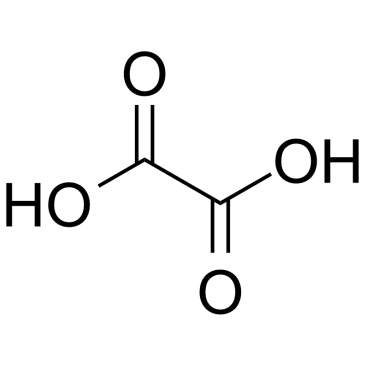 |
Oxalic acid
CAS:144-62-7 |
|
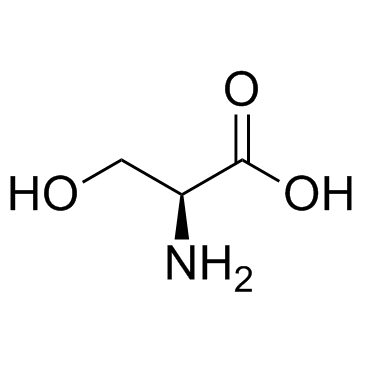 |
L-serine
CAS:56-45-1 |
|
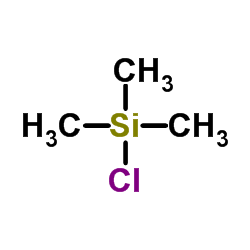 |
Chlorotrimethylsilane
CAS:75-77-4 |