| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
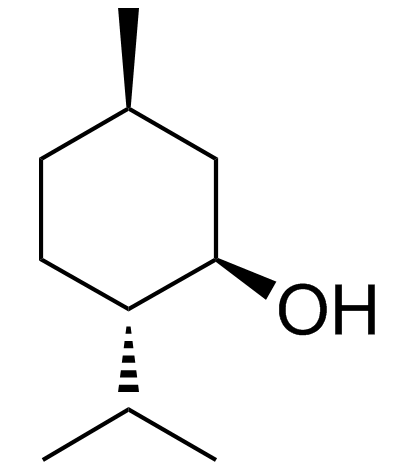 |
L-Menthol
CAS:2216-51-5 |
|
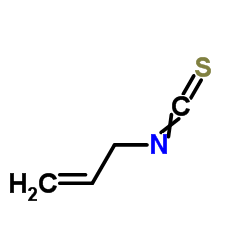 |
Allyl isothiocyanate
CAS:57-06-7 |
|
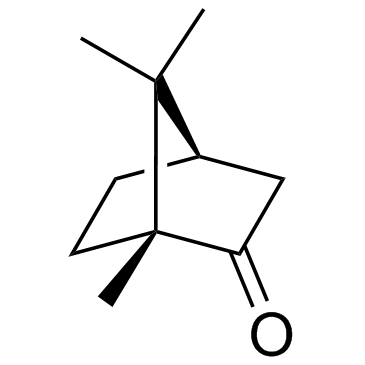 |
(+)-Camphor
CAS:464-49-3 |
|
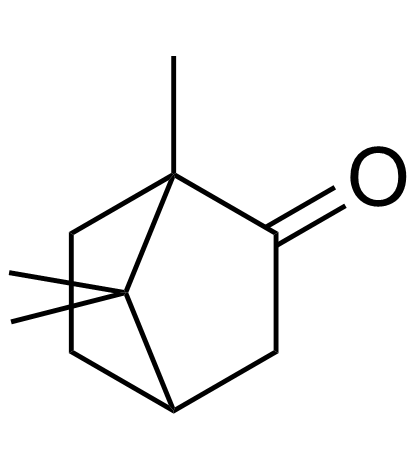 |
(+/-)-Camphor
CAS:76-22-2 |
|
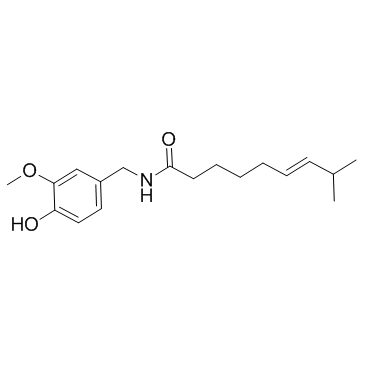 |
capsaicin
CAS:404-86-4 |
|
 |
Cinnamic aldehyde
CAS:14371-10-9 |
|
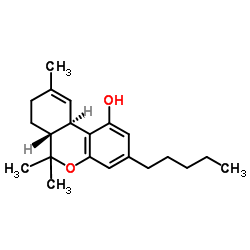 |
(-)-δ9-trans-Tetrahydrocannabinol
CAS:1972-08-3 |
|
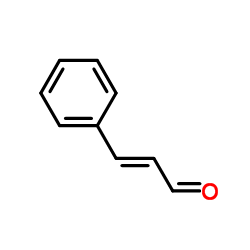 |
Cinnamaldehyde
CAS:104-55-2 |
|
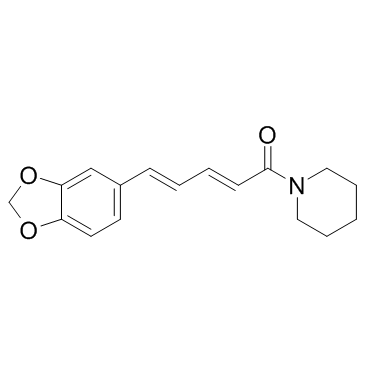 |
Piperine
CAS:94-62-2 |