Indole-2-carboxylic acid
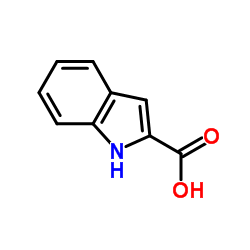
Indole-2-carboxylic acid structure
|
Common Name | Indole-2-carboxylic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1477-50-5 | Molecular Weight | 161.157 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 419.6±18.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7NO2 | Melting Point | 202-206 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 207.6±21.2 °C | |
Use of Indole-2-carboxylic acidIndole-2-carboxylic acid is a strong inhibitor of lipid peroxidation. Indole-2-carboxylic acid (I2CA) specifically and competitively inhibits the potentiation by glycine of NMDA-gated current[1][2]. |
| Name | Indole-2-carboxylic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Indole-2-carboxylic acid is a strong inhibitor of lipid peroxidation. Indole-2-carboxylic acid (I2CA) specifically and competitively inhibits the potentiation by glycine of NMDA-gated current[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 419.6±18.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 202-206 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 161.157 |
| Flash Point | 207.6±21.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 161.047684 |
| PSA | 53.09000 |
| LogP | 2.31 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.726 |
| InChIKey | HCUARRIEZVDMPT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)c1cc2ccccc2[nH]1 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant;Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NK7882812 |
| HS Code | 29339990 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Molecular modifications on carboxylic acid derivatives as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: Activity and docking studies.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 5219-28, (2009) In the light of known HDAC inhibitors, 33 carboxylic acid derivatives were tested to understand the structural requirements for HDAC inhibition activity. Several modifications were applied to develop ... |
|
|
In vitro and in vivo assessment of the antioxidant activity of melatonin and related indole derivatives.
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 21(2) , 153-62, (2002) Effects of melatonin and some structurally related indole compounds were studied by in vitro methods such as (i) an inhibition of the hyaluronic acid degradation and (ii) a standard lipid peroxidation... |
|
|
Protonated carbonic acid and reactive intermediates in the acidic decarboxylation of indolecarboxylic acids.
J. Org. Chem. 77(15) , 6505-9, (2012) Elucidation of the mechanism for decarboxylation of indolecarboxylic acids over a wide range of solution acidity reveals the importance of protonated carbonic acid (PCA) as a reaction intermediate. In... |
| 1H-Indole-2-carboxylic acid |
| T56 BMJ CVQ |
| Indole-2-carboxylic acid |
| 2-Carboxyindole |
| 2-Indolecarboxylic acid |
| MFCD00005611 |
| EINECS 216-030-4 |
 CAS#:3770-50-1
CAS#:3770-50-1 CAS#:19005-93-7
CAS#:19005-93-7 CAS#:615-43-0
CAS#:615-43-0 CAS#:127-17-3
CAS#:127-17-3 CAS#:40899-93-2
CAS#:40899-93-2 CAS#:615-36-1
CAS#:615-36-1![Pyrazino[1,2-a;4,5-a]diindole-6,13-dione Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/054/58881-41-7.png) CAS#:58881-41-7
CAS#:58881-41-7 CAS#:26340-49-8
CAS#:26340-49-8 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:120-72-9
CAS#:120-72-9 CAS#:103476-80-8
CAS#:103476-80-8 CAS#:5055-39-0
CAS#:5055-39-0 CAS#:32588-36-6
CAS#:32588-36-6 CAS#:14255-18-6
CAS#:14255-18-6 CAS#:1485-22-9
CAS#:1485-22-9 CAS#:101125-32-0
CAS#:101125-32-0 CAS#:141306-08-3
CAS#:141306-08-3 CAS#:4264-35-1
CAS#:4264-35-1 CAS#:17537-64-3
CAS#:17537-64-3 CAS#:703-80-0
CAS#:703-80-0