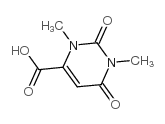
65-86-1
| Name | orotic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Orotonsan
orotic Oropur 2,6-dihydroxypyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid Uracil-6-carboxylic acid Orotic acid [3H]-Orotic acid vitamin B13 Oroturic H-ORO-OH Orotsaure MFCD00006027 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidine carboxylic acid EINECS 200-619-8 2,6-Dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid 1,2,3,6-TETRAHYDRO-2,6-DIOXO-4-PYRIMIDINECARBOXYLIC ACID 2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid Orotonin Whey factor Orotyl Orodin 6-Carboxyuracil orodin[qr] 6-uracilic acid 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydro-2,6-dioxopyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid Animal galactose factor |
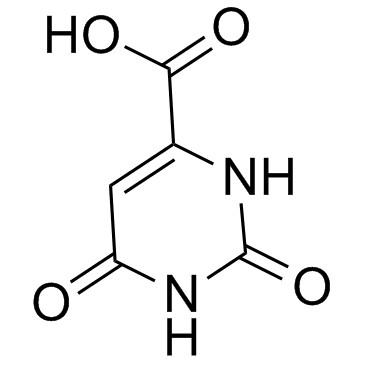
| Description | Orotic acid (OA) is an intermediate in pyrimidine metabolism.IC50 Value: Target: Nucleoside antimetabolite/analogin vitro: OA increases cell proliferation and decreases apoptosis in serum-starved SK-Hep1 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, which may ascribe to the inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and thus activation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) [1].in vivo: male Fischer 344 rats (130-150 g) to two-thirds PH in the absence or in the presence of OA (a 300-mg tablet of OA methyl ester implanted intraperitoneally at the time of two-thirds PH). treatment with OA resulted in a near-100% inhibition of RNR induced by two-thirds PH in rat liver, as monitored by enzyme activity and protein level [2]. The increases of hepatic OA and betaine levels in OA feeding rats was also found when compared to the normal rats [3]. Feeding 1% OA with diet decreased the phosphorylation of AMPK and increased the maturation of SREBP-1 and the expression of SREBP-responsive genes in the rat liver. OA-induced lipid accumulation was also completely inhibited by rapamycin. Mouse hepatocytes and mice were resistant to OA-induced lipogenesis because of little if any response in AMPK and downstream effectors [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 656.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300°C |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 156.096 |
| Flash Point | 351.1±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 156.017105 |
| PSA | 103.02000 |
| LogP | -1.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.705 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RM3180000 |
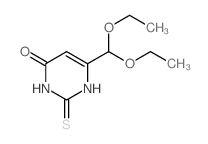
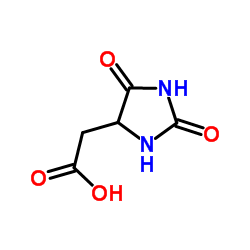
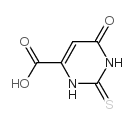
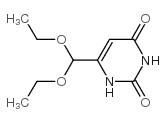
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |




![Furo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-2,4,7(3H)-trione,1,5-dihydro structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/254/4156-75-6.png)