Orotic acid
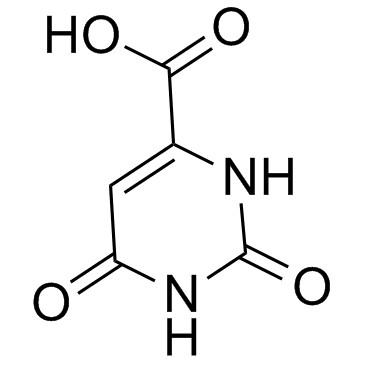
Orotic acid structure
|
Common Name | Orotic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 65-86-1 | Molecular Weight | 156.096 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 656.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N2O4 | Melting Point | >300°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 351.1±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Purity | Quantity | Budget | Inquiry |
|---|
Use of Orotic acidOrotic acid (OA) is an intermediate in pyrimidine metabolism.IC50 Value: Target: Nucleoside antimetabolite/analogin vitro: OA increases cell proliferation and decreases apoptosis in serum-starved SK-Hep1 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, which may ascribe to the inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and thus activation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) [1].in vivo: male Fischer 344 rats (130-150 g) to two-thirds PH in the absence or in the presence of OA (a 300-mg tablet of OA methyl ester implanted intraperitoneally at the time of two-thirds PH). treatment with OA resulted in a near-100% inhibition of RNR induced by two-thirds PH in rat liver, as monitored by enzyme activity and protein level [2]. The increases of hepatic OA and betaine levels in OA feeding rats was also found when compared to the normal rats [3]. Feeding 1% OA with diet decreased the phosphorylation of AMPK and increased the maturation of SREBP-1 and the expression of SREBP-responsive genes in the rat liver. OA-induced lipid accumulation was also completely inhibited by rapamycin. Mouse hepatocytes and mice were resistant to OA-induced lipogenesis because of little if any response in AMPK and downstream effectors [4]. |
| Name | orotic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Orotic acid (OA) is an intermediate in pyrimidine metabolism.IC50 Value: Target: Nucleoside antimetabolite/analogin vitro: OA increases cell proliferation and decreases apoptosis in serum-starved SK-Hep1 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, which may ascribe to the inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and thus activation of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) [1].in vivo: male Fischer 344 rats (130-150 g) to two-thirds PH in the absence or in the presence of OA (a 300-mg tablet of OA methyl ester implanted intraperitoneally at the time of two-thirds PH). treatment with OA resulted in a near-100% inhibition of RNR induced by two-thirds PH in rat liver, as monitored by enzyme activity and protein level [2]. The increases of hepatic OA and betaine levels in OA feeding rats was also found when compared to the normal rats [3]. Feeding 1% OA with diet decreased the phosphorylation of AMPK and increased the maturation of SREBP-1 and the expression of SREBP-responsive genes in the rat liver. OA-induced lipid accumulation was also completely inhibited by rapamycin. Mouse hepatocytes and mice were resistant to OA-induced lipogenesis because of little if any response in AMPK and downstream effectors [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 656.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300°C |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 156.096 |
| Flash Point | 351.1±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 156.017105 |
| PSA | 103.02000 |
| LogP | -1.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.705 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RM3180000 |
|
Solubilization of gliadins for use as a source of nitrogen in the selection of bacteria with gliadinase activity.
Food Chem. 168 , 439-44, (2014) For patients with celiac disease, gliadin detoxification via the use of gliadinases may provide an alternative to a gluten-free diet. A culture medium, in which gliadins were the sole source of nitrog... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
QSPR modeling of octanol/water partition coefficient for vitamins by optimal descriptors calculated with SMILES.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43 , 714-40, (2008) Simplified molecular input line entry system (SMILES) has been utilized in constructing quantitative structure-property relationships (QSPR) for octanol/water partition coefficient of vitamins and org... |
| Orotonsan |
| orotic |
| Oropur |
| 2,6-dihydroxypyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid |
| Uracil-6-carboxylic acid |
| Orotic acid |
| [3H]-Orotic acid |
| vitamin B13 |
| Oroturic |
| 4-Pyrimidinecarboxylic acid, 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-2,6-dioxo- |
| H-ORO-OH |
| Orotsaure |
| MFCD00006027 |
| 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidine carboxylic acid |
| EINECS 200-619-8 |
| 2,6-Dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid |
| 1,2,3,6-TETRAHYDRO-2,6-DIOXO-4-PYRIMIDINECARBOXYLIC ACID |
| 2,6-dioxo-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid |
| Orotonin |
| Whey factor |
| Orotyl |
| Orodin |
| 6-Carboxyuracil |
| orodin[qr] |
| 6-uracilic acid |
| 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydro-2,6-dioxopyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid |
| Animal galactose factor |
 CAS#:5988-19-2
CAS#:5988-19-2 CAS#:5962-07-2
CAS#:5962-07-2 CAS#:298-12-4
CAS#:298-12-4 CAS#:119767-58-7
CAS#:119767-58-7 CAS#:16953-46-1
CAS#:16953-46-1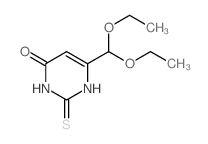 CAS#:16953-49-4
CAS#:16953-49-4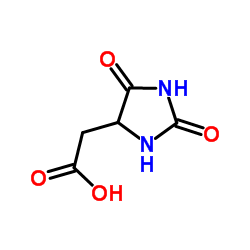 CAS#:5427-26-9
CAS#:5427-26-9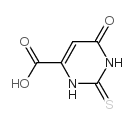 CAS#:6953-78-2
CAS#:6953-78-2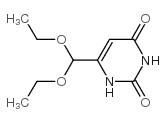 CAS#:16953-48-3
CAS#:16953-48-3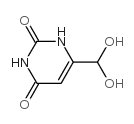 CAS#:36327-91-0
CAS#:36327-91-0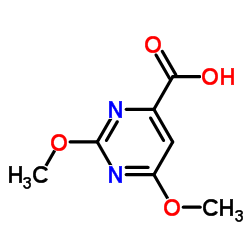 CAS#:59864-30-1
CAS#:59864-30-1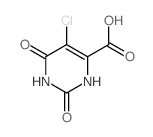 CAS#:36313-98-1
CAS#:36313-98-1![Furo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-2,4,7(3H)-trione,1,5-dihydro- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/254/4156-75-6.png) CAS#:4156-75-6
CAS#:4156-75-6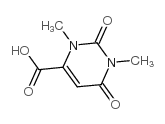 CAS#:4116-38-5
CAS#:4116-38-5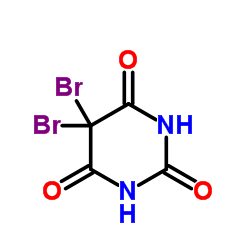 CAS#:511-67-1
CAS#:511-67-1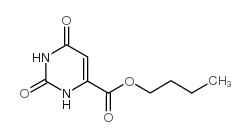 CAS#:22754-37-6
CAS#:22754-37-6 CAS#:58-97-9
CAS#:58-97-9 CAS#:66-22-8
CAS#:66-22-8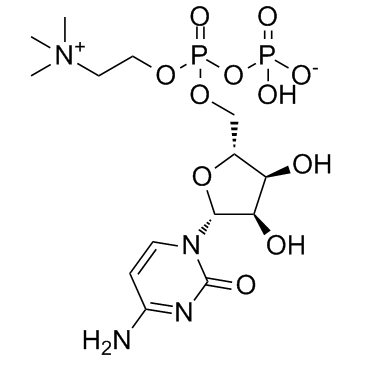 CAS#:987-78-0
CAS#:987-78-0
