65-46-3
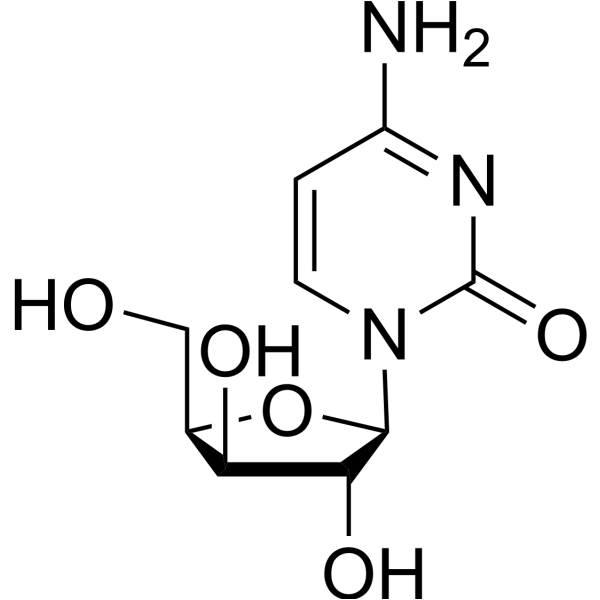
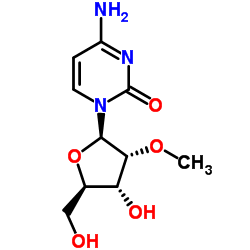
| Name | Cytidine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
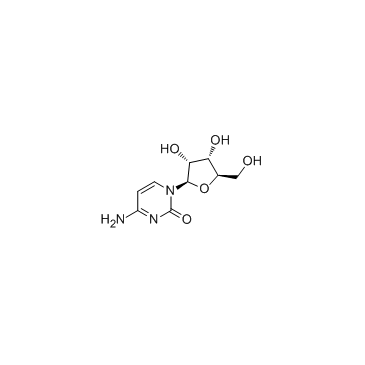
1-(b-D-Ribofuranosyl)-2-oxo-4-amino-1,2-dihydro-1,3-diazine
EINECS 200-610-9 4-Amino-1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-2(1H)-pyrimidinone 1-β-D-Ribofuranosylcytosine 4-Amino-1-β-δ-ribofuranosyl-2(1H)-pyrimidinone 4-Amino-1-(β-D-ribofuranosyl)pyrimidin-2(1H)-on MFCD02181091 Cytidine 4-Amino-1-b-D-ribofuranosyl-2(1H)-pyrimidinone Cyd Cytidin 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-Cytosine Citidine 1-(b-δ-Ribofuranosyl)-2-oxo-4-amino-1,2-dihydro-1,3-diazine d-cytidine 1-β-δ-Ribofuranosylcytosine CYTIDINE extrapure 1-b-D-Ribofuranosylcytosine 4-Imino-1-(β-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,4-dihydro-2-pyrimidinol |
| Description | Cytidine is a nucleoside molecule that is formed when cytosine is attached to a ribose ring, cytidine is a component of RNA.Target: Nucleoside antimetabolite/analogCytidine is a nucleoside molecule that is formed when cytosine is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond. Cytidine is a component of RNA. If cytosine is attached to a deoxyribose ring, it is known as a deoxycytidine. Dietary sources of cytidine include foods with high RNA (ribonucleic acid) content, such as organ meats, Brewer's yeast, as well as pyrimidine-rich foods such as beer. During digestion, RNA-rich foods are broken-down into ribosyl pyrimidines (cytidine and uridine), which are absorbed intact. In humans, dietary cytidine is converted into uridine, which is probably the compound behind cytidine's metabolic effects.There are a variety of cytidine analogs with potentially useful pharmacology. For example, KP-1461 is an anti-HIV agent that works as a viral mutagen, and zebularine exists in E. coli and is being examined for chemotherapy. Low doses of azacitidine and its analog decitabine have shown results against cancer through epigenetic demethylation. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
[1]. Jonas DA, et al. Safety considerations of DNA in food. Ann Nutr Metab. 2001;45(6):235-54. |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 529.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 210-220 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 243.217 |
| Flash Point | 274.1±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 243.085526 |
| PSA | 130.83000 |
| LogP | -1.78 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.756 |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | F+ |
| Risk Phrases | R68 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UW7370000 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |