802918-57-6
| Name | silibinin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
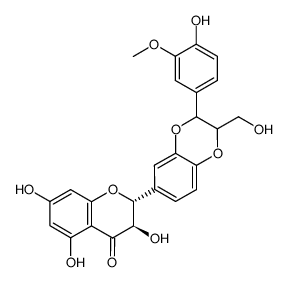
(2R,3R)-2-[2,3-dihydro-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl]-2,3-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
silibin silybin Silybin Silybin A,B (mixture) |
| Description | Silybin is a flavonolignan isolated from milk thistle (Silybum marianum) seeds. Silybin induces apoptosis and exhibits hepatoprotective, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer activity[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Silybin (0-200 mM; for 72 hours) has growth inhibition in a time- and dose-dependent manner[1]. Silybin (68 μM; for 72 hours) induces apoptosis and increases the cells in G1-phase of ~22%[1]. Silybin (68 μM; for 72 hours) induces AKT activity inhibition[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: HepG2 cell growth Concentration: 0-200 mM Incubation Time: For 72 hours Result: Had growth inhibition in a time- and dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 68 μM. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: HepG2 cell growth Concentration: 68 μM Incubation Time: For 72 hours Result: Induced apoptosis in a higher number of cells (60%) when compared to untreated cells. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: HepG2 cell growth Concentration: 68 μM Incubation Time: For 72 hours Result: Increased the cells in G1-phase of ~22% and decreased of 47% the cells in S-phase. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: HepG2 cell growth Concentration: 68 μM Incubation Time: For 72 hours Result: Induced AKT activity inhibition. |
| In Vivo | Silybin (50, 100 mg/kg/day; given intragastrically for the last 4 weeks) significantly lowers both serum and hepatic lipid accumulation[2]. Animal Model: Male C57BL/6J mice (6-8 weeks old) with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[2] Dosage: 50, 100 mg/kg Administration: Given intragastrically; daily; for the last 4 weeks Result: Significantly lowered both serum and hepatic lipid accumulation. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 152-153°C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H22O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 482.43600 |
| Exact Mass | 482.12100 |
| PSA | 155.14000 |
| LogP | 2.36270 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | DJ2981770 |