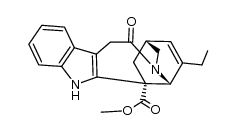
2468-21-5
| Name | catharanthine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Methyl (2α,5β,18β)-3,4-didehydroibogamine-18-carboxylate
Catharanthine Sulphate catharintine CatharanthineSulfateBase catharantine (2α,5β,6α,18β)-3,4-Didehydroibogamine-18-carboxylic acid methyl ester (+)-3,4-Didehydrocoronaridine Catharanthine catharanthin UNII-WT0YJV846J catharinthine MFCD01753356 |
| Description | Catharanthine inhibits nicotinic receptor mediated diaphragm contractions with IC50 of 59.6 μM.Target: nAChRCatharanthine evokes a concentration-dependent attenuation of carbachol responses in the rat ileum preparation, producing rightward curve displacements and decreases in maximal agonist responses. The mixture of serpentine, plus ajmalicine and catharanthine reveals a concentration-dependent inhibitory effect of acethylcholinesterase (AchE), with an IC50 at ca. 2.25 μg/Ml [1]. Catharanthine can induce the self-association of tubulin into linear indefinite polymers with an efficacy that is 75% that of vinblastine or vincristine. Catharanthine binds to tubulin alpha-beta dimer with binding constant of 2.8 mM [2]. Catharanthine stimulates release of amylase from pancreatic fragments and to cause extensive degranulation of pancreatic acinar cells with accumulation of membrane material in the Golgi region. Catharanthine induces a delayed release of Ca2+ from prelabeled pancreatic fragments as compared to bethanechol [3]. Catharanthine inhibits epibatidine-induced Ca(2+) influx in TE671-α, -β, -γ, -δ cells in a noncompetitive manner with similar potencies IC50 of 17 mM-25 mM. Catharanthine inhibits [3H]TCP binding to the desensitized Torpedo AChR with higher affinity compared to the resting AChR. Catharanthine enhances [3H]cytisine binding to resting but activatable Torpedo AChRs, suggesting desensitizing properties [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 491.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 138-140ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C21H24N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 336.427 |
| Flash Point | 251.1±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 336.183777 |
| PSA | 45.33000 |
| LogP | 4.05 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.663 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~96% 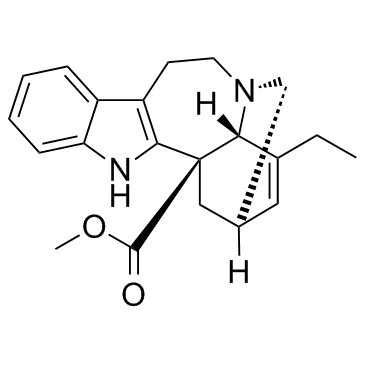
2468-21-5 |
| Literature: Szantay, Csaba; Boelcskei, Hedvig; Gacs-Baitz, Eszter Tetrahedron, 1990 , vol. 46, # 5 p. 1711 - 1732 |
|
~% 
2468-21-5 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 46, # 5 p. 1711 - 1732 |
|
~% 
2468-21-5 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 46, # 5 p. 1711 - 1732 |
|
~% 
2468-21-5 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 46, # 5 p. 1711 - 1732 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |