31852-29-6
| Name | POLYINOSINIC-POLYCYTIDYLIC ACID POTASSIUM SALT |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MFCD00131983 |
| Description | Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium (Poly(I:C) potassium) is a synthetic analog of double-stranded RNA and an agonist of toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and retinoic acid inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RIG-I and MDA5). Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid sodium can be used as a vaccine adjuvant to enhance innate and adaptive immune responses, and to alter the tumor microenvironment. Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium can directly trigger cancer cells to undergoApoptosis[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TLR3 |
| In Vitro | Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium (20 ng/mL; 24 hours; WM793, WM278, WM239A, WM9 and 1205Lu cells) 抑制细胞生长活性[1]. Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium (200 ng/mL; 24 hours; 1205Lu cells) 诱导 1205Lu 细胞凋亡[1]。 Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium (5 ng/mL; 24 hours; 1205Lu cells) 诱导黑素瘤细胞中的 IFN-β 表达。RIG-I 和 MDA-5 的沉默证实 Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium 诱导 IFN-β 分别需要 RIG-I 和 MDA-5,并且需要 IPS-1[1]。 Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium 重悬于无菌盐水中,以 2 mg/ml 的浓度加热至 50 °C 以确保完全溶解,然后自然冷却至室温以确保双链 RNA 的适当退火,从而制备用于注射的 Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium. Poly I:C 储存在 -20 °C 直至使用[3]。 Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: WM793, WM278, WM239A, WM9 and 1205Lu cells Concentration: 20 ng/mL Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Strongly reduced viability from 100% in controls to 20%–50% within 24 hours. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: 1205Lu cells Concentration: 200 ng/mL Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Induced apoptosis in 1205Lu cells. RT-PCR[1] Cell Line: WM793, WM278, WM239A, WM9 and 1205Lu cells Concentration: 3 ng/mL Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Induced IFN-β expression in melanoma cells. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: 1205Lu cells Concentration: 5 ng/mL Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Revealed active subunits of caspase-9 and caspase-8 in melanoma cells. |
| In Vivo | Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid potassium (50 µg; i.v.; on days 3, 6, and 9 after tumor inoculation) 在 NOD/SCID 免疫缺陷小鼠中显示出抗肿瘤活性[1]。 Animal Model: NOD/SCID immunodeficient mice (1205Lu cells)[1] Dosage: 50 µg Administration: I.v.; on days 3, 6, and 9 after tumor inoculation Result: Reduced the size of metastases and the total amount of tumor tissue, and the level of human DNA was 50% lower in mice. |
| References |
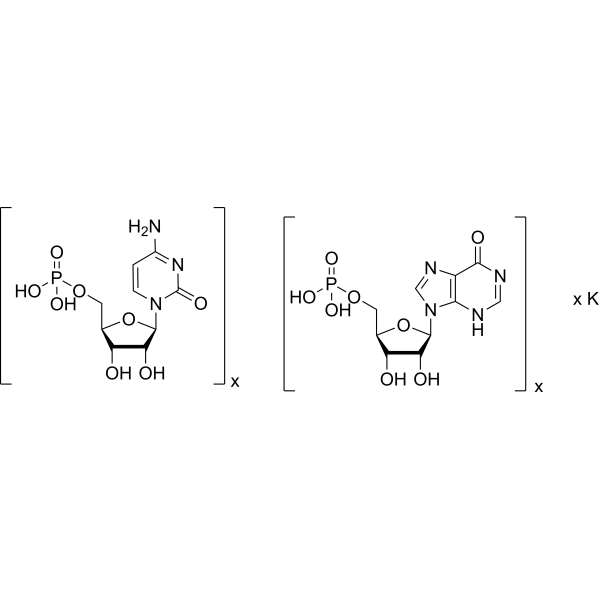
| Molecular Formula | (C10H13N4O8P)x.(C9H14N3O8P)x.xK |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 710.5 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |