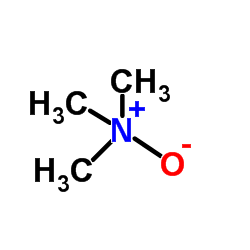
1184-78-7
| Name | trimethylamine N-oxide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
TMAO
N,N-Dimethylmethanamine N-oxide EINECS 214-675-6 Triox anhydrous trimethylamine oxide TriMethylaMine N-Oxide N,N-dimethylmethanamine oxide Methanamine,N,N-dimethyl-,N-oxide trimethylamine-N-oxide Trimethylamine oxide Triméthylamine-oxyde Trimethylamineoxid MFCD00002048 Trimethyloxamine |
| Description | Trimethylamine N-oxide is a gut microbe-dependent metabolite of dietary choline and other trimethylamine-containing nutrients. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation by activating the ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome. Trimethylamine N-oxide also accelerates fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation and induces cardiac fibrosis by activating the TGF-β/smad2 signaling pathway[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome[1] TGF-β/smad2[1] |
| In Vitro | The size and migration of fibroblasts are increased after Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) treatment compared with non-treated fibroblasts in vitro. Trimethylamine N-oxide increases TGF-β receptor I expression, which promotes the phosphorylation of Smad2 and up-regulates the expression of α-SMA and collagen I. The ubiquitination of TGF-βRI is decreased in neonatal mouse fibroblasts after Trimethylamine N-oxide treatment. Trimethylamine N-oxide also inhibits the expression of smurf2[2]. Trimethylamine N-oxide is frequently found in the tissues of a variety of marine organisms that protects against the adverse effects of temperature, salinity, high urea and hydrostatic pressure[3]. |
| In Vivo | Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) contributes to cardiovascular diseases by promoting inflammatory responses. C57BL/6 mice are fed a normal diet, high-choline diet and/or 3-dimethyl-1-butanol (DMB) diet. The levels of Trimethylamine N-oxide and choline are increased in choline-fed mice. Left ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonary congestion, and diastolic dysfunction are markedly exacerbated in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) mice fed high-choline diets compared with mice fed the control diet. Myocardial fibrosis and inflammation were markedly increased in HFpEF mice fed high-choline diets compared with animals fed the control diet[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9301 (rough estimate) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 133.8°C (rough estimate) |
| Melting Point | 220-222ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H9NO |
| Molecular Weight | 75.110 |
| Exact Mass | 75.068413 |
| PSA | 29.43000 |
| LogP | -2.57 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.4698 (estimate) |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2921110090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921110090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2921110090. methylamine, di- or trimethylamine and their salts. VAT:17.0%. tax rebate rate:9.0%. supervision conditions:ab(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward). MFN tariff:6.5%. general tariff:30.0% |