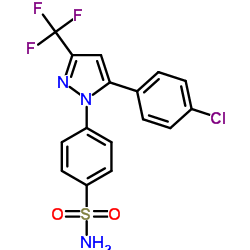
170569-86-5
| Name | 4-[5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
HMS3262A06
4-[5-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]-benzenesulfonamide SC-58236 Tracazolate hydrochloride SC236 4-[5-(4-chorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide 4-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-yl)benzenesulfonamide 4-[5-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonamide 4-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide |
| Description | SC-236 is an orally active COX-2 specific inhibitor (IC50 = 10 nM) and a PPARγ agonist. SC-236 suppresses activator protein-1 (AP-1) through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. SC-236 exerts anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing phosphorylation of ERK in a murine model[1][2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-2:10 nM (IC50) COX-1:17.8 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | SC-236 (15 μM, 30 min) suppresses the side effects of NSAIDs and prevented inflammation in vECs subjected to ALSS[1]. SC-236 significantly induces PPARγ expression in HSCs and acted as a potent PPARγ agonist in a luciferase-reporter trans-activation assay[2]. SC-236 strongly inhibits, in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, macrophageviability[2]. SC-236, either alone or in combination with 15d-PGJ2, induced a marked pro-apoptotic effect in HSCs in culture[2]. SC-236 mediates antitumor effect by modulation of AP-1-signaling pathway[3]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: vECs. Concentration: 15 μM Incubation Time: 30 min. Result: Showd significant reduction in COX-2 level and increase in IκBα level, thus preventing ALSS-induced NFκB activation and inflammation in vECs. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: COS 7 cells. Concentration: 3 and 10 μM. Incubation Time: 18 h (combined with 15d-PGJ2). Result: Acted in a concentration-dependent manner as a PPARγ agonist. |
| In Vivo | SC-236 (6 mg/kg, gavage) exhibits anti-fibrotic properties in CCl4- treated animals[2]. Animal Model: Seventy-six male adult Wistar rats weighing 200-220 g (CCl4-treated)[2]. Dosage: 6 mg/kg. Administration: Orally, 3 times per week. Result: A marked induction of COX-2 protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry in the liver of CCl4-treated rats. Significantly reduced the degree of liver fibrosis. Dramatically suppressed α-SMA expression in CCl4-treated rats. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 543.4±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C16H11ClF3N3O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 401.791 |
| Flash Point | 282.4±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 401.021271 |
| PSA | 86.36000 |
| LogP | 4.32 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.625 |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
| HS Code | 2935009090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2935009090 other sulphonamides VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:35.0% |