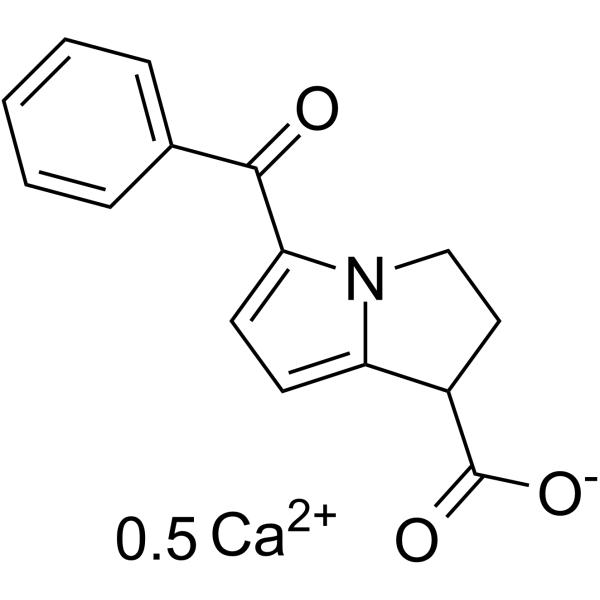
| Description |
Ketorolac (RS37619) hemicalcium is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), acting as a nonselective COX inhibitor, with IC50s of 20 nM for COX-1 and 120 nM for COX-2. Ketorolac tromethamine is used as 0.5% ophthalmic solution for the research of allergic conjunctivitis, cystoid macular edema, intraoperative miosis, and postoperative ocular inflammation and pain. Ketorola chemicalcium is also a DDX3 inhibitor that can be used for cancer research[1][4].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
Ketorolac (RS37619) salt (0-30 μM, 48 h) effectively kills the oral cancer cells[4]. Ketorolac salt (0-5 μM, 48 h) inhibits the expression of DDX3 protein, and induces apoptosis in H357 cells[4]. Ketorolac salt (0-2.5 μM, 0-16 h) inhibits the proliferation of oral cancer cells[4]. Ketorolac salt (0-50 μM) directly interacts with DDX3 and inhibits the ATPase activity[4]. Cell Viability Assay[4] Cell Line: HOK, SCC4, SCC9 and H357 cells Concentration: 0-30 μM Incubation Time: 48 h Result: Showed inhibition with IC50s of 2.6, 7.1 and 8.1 μM against H357, SCC4 and SCC9 cells, respectively. And the normal HOK cell line did not show any cell death effect. Cell Proliferation Assay[4] Cell Line: H357 Concentration: 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 and 2.5 μM Incubation Time: 0, 8 and 16 h Result: Inhibited the proliferation. Western Blot Analysis[4] Cell Line: H357 Concentration: 1, 2.5 and 5 μM Incubation Time: 48 h Result: Significantly reduced DDX3 protein expression levels, but not completely ablated as compared to DMSO treated cells. Up regulated the expression of E-cadherin. Apoptosis Analysis[4] Cell Line: H357 Concentration: 2.5 and 5 μM Incubation Time: 48 h Result: Induced apoptosis.
|
| In Vivo |
Ketorolac (RS37619) (0.4% ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) shows powerful ocular anti-inflammatory activities in rabbits[1]. Ketorolac (4 mg/kg/day, p.o.; 2 weeks) has no detrimental effect in the volume fraction of bone trabeculae formed inside the alveolar socket in rats[2]. Ketorolac (60 μg; intrathecal injection; once) attenuates the damage caused by spinal cord ischemia in rats[3]. Ketorolac salt (20 and 30 mg/kg; i.p.; two times in a week for 3 weeks) reduces oral carcinogenesis in mice[4]. Animal Model: New Zealand White rabbits (2.0–2.7 kg), LPS endotoxin-induced ocular inflammation[1] Dosage: 50 μL ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.4% Administration: In eyes, twice, 2 hours and 1 hour before LPS challenge Result: Resulted in a nearly complete inhibition (98.7%) of LPS endotoxin-induced increases in FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate)-dextran in the anterior chamber, and resulted in a nearly complete inhibition (97.5%) of LPS endotoxin-induced increases in aqueous PGE2 concentrations in the aqueous humor. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats (400–450 g), spinal cord ischemia model[3] Dosage: 30 and 60 μg Administration: Intrathecal injection, 1 h before the ischemia induction for once Result: Significantly reduced the motor disturbances and improved the survival rate at 60 μg. Animal Model: BALB/c mice, oral carcinogenesis model[4] Dosage: 20 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg Administration: IP injection, two times in a week for 3 weeks Result: Decreased tumor burden, reduced expression of DDX3 and anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2 and Mcl-1).
|
| References |
[1]. Waterbury LD, et al. Comparison of cyclooxygenase inhibitory activity and ocular anti-inflammatory effects of ketorolac tromethamine and bromfenac sodium. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006 Jun;22(6):1133-40. [2]. Fracon RN, et al. Treatment with paracetamol, ketorolac or etoricoxib did not hinder alveolar bone healing: a histometric study in rats. J Appl Oral Sci. 2010 Dec;18(6):630-4. [3]. Hsieh YC, et al. Intrathecal ketorolac pretreatment reduced spinal cord ischemic injury in rats. Anesth Analg. 2005 Apr;100(4):1134-9. [4]. Samal SK, et al. Ketorolac salt is a newly discovered DDX3 inhibitor to treat oral cancer. Sci Rep. 2015 Apr 28;5:9982.
|