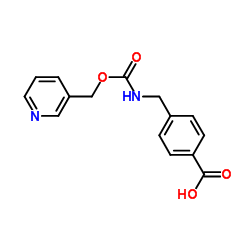
209783-80-2
| Name | N-(2-aminophenyl)-4-[N-(pyridin-3-yl)methoxycarbonylaminomethyl]benzamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Entinostat (MS-275)
MS-275 SNDX-275 Entinostat pyridin-3-ylmethyl 4-((2-aminophenyl)carbamoyl)benzylcarbamate Entinostat (MS-275,SNDX-275) 3-Pyridinylmethyl {4-[(2-aminophenyl)carbamoyl]benzyl}carbamate Pyridin-3-ylmethyl {4-[(2-aminophenyl)carbamoyl]benzyl}carbamate Carbamic acid, N-[[4-[[(2-aminophenyl)amino]carbonyl]phenyl]methyl]-, 3-pyridinylmethyl ester N-(2-Aminophenyl)-4-[N-(pyridine-3-ylmethoxycarbonyl)aminomethyl]benzamide MS 275-27 ((4-(((2-Aminophenyl)amino)carbonyl)phenyl)methyl)carbamic Acid 3-Pyridinylmethyl Ester |
| Description | Entinostat is an oral and selective class I HDAC inhibitor, with IC50s of 243 nM, 453 nM, and 248 nM for HDAC1, HDAC2, and HDAC3, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
HDAC1:243 nM (IC50) HDAC3:248 nM (IC50) HDAC2:453 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Binding affinity of Entinostat (MS-275) against HDAC1 and HDAC2 is 282 nM and 156 nM, respectively[1]. Effects of the HDAC inhibitor Entinostat (MS-275) have been examined in human leukemia and lymphoma cells (U937, HL-60, K562, and Jurkat) as well as in primary acute myelogenous leukemia blasts in relation to differentiation and apoptosis. MS-275 displays dose-dependent effects in each of the cell lines. When administered at a low concentration (e.g., 1 μM), MS-275 exhibits potent antiproliferative activity, inducing p21CIP1/WAF1-mediated growth arrest and expression of differentiation markers (CD11b) in U937 cells. Entinostat (MS-275) potently induces cell death, triggering apoptosis in ~70% of cells at 48 h[2]. |
| In Vivo | Entinostat (MS-27-275) at 49 mg/kg shows marked antitumor effects against KB-3-1, 4-1St, and St-4 tumor lines, and a moderate effect against Capan-1 tumor. Entinostat at 24.5 mg/kg and 12.3 mg/kg also shows significant effects against these tumors. In addition, oral administration of Entinostat apparently increases the level of histone acetylation in HT-29 tumor xenografts 4-24 h after the administration[3]. MS-275 administration (3.5 mg/kg i.p.) to Experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN) rats once daily from the appearance of first neurological signs greatly reduces the severity and duration of EAN and attenuated local accumulation of macrophages, T cells and B cells, anddemyelination of sciatic nerves. Further, significant reduction of mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory interleukin-1β, interferon-γ, interleukine-17, inducible nitric oxide synthaseand matrix metalloproteinase-9 is observed in sciatic nerves of MS-275 treated EAN rats. In addition, MS-275 treatment increases proportion of infiltrated Foxp3+ cells and anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages in sciatic nerves of EAN rats[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Biochemical assays of HDAC activity are carried out by Nanosyn in a reaction volume of 10 μL in 384-well microplates. A standard enzymatic reaction contains 5 μL of 2× HDAC inhibitor (e.g., Entinostat), 4 μL of 2.5× enzyme, and 1 μL of 10× substrate in assay buffer (100 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 25 mM KCl, 0.1% BSA, 0.01% Triton X-100, 1% DMSO). Final concentration of all HDACs in the enzymatic assays is between 0.5 and 5 nM. A final substrate concentration of 1 μM FAM-RHKK(Ac)-NH2 or FAM-RHKK(trifluoroacetyl)-NH2 is used in all assays and found to be below the determined Km,app for each enzyme[1]. |
| Cell Assay | SH-SY5Y cells are maintained under normal culture conditions in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2 and are split twice weekly. Cells are plated in black 384-well plates at 2500 cells/well in 20-μL volume of DMEM/F-12 culture media supplemented with 10% FBS and permitted to adhere overnight. The following day, HDAC inhibitors (e.g., Entinostat) are serially diluted in 100% DMSO, and this series is subsequently cross-diluted into culture media. 5 μL of compound (e.g., Entinostat) diluted in media is added to the appropriate well of the cell plate to afford the indicated final concentration of inhibitor (e.g., Entinostat) with a final 0.1% DMSO. Treated cells are incubated under normal tissue culture conditions for 6, 24, 48, 72, or 96 h prior to quantitation of cellular ATP levels as measured using CellTiter-Glo reagents. Similarly, after 6 h of incubation with HDAC inhibitors (e.g., Entinostat), media from separate cell plates are aspirated, and cells are washed once with media containing no inhibitors. 25 μL of media supplemented with 10% FBS and 0.1% DMSO (no inhibitors) is added back to the cells, and cellular ATP levels are determined using CellTiter-Glo after 24, 48, 72, or 96 h of incubation. Luminescence is measured at each time point using an Envision Instrument with a 0.1 s count time[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] A2780 cells (9×106) are suspended in PBS and are injected subcutaneously into the flank of nude mouse. For the other tumor lines, KB-3-1, HCT-15, 4-1St, Calu-3, St-4, Capan-1, and HT-29, tumors are passaged several times before starting in vivo antitumor testing, and a tumor lump (2-3 mm in diameter) is transplanted subcutaneously into the flank of a nude mouse by using a trocar needle. Treatment (four or five mice in each experimental group) with the drugs is started after the tumors are confirmed to have grown in the body (tumor size, 20-100 mm3). Entinostat is administered orally once daily 5 days per week for 4 weeks. Tumor length and width are monitored twice weekly, and tumor volume is calculated. Rats[4] Male Lewis rats (8-10 weeks, 170-200 g) are housed under a 12-h light/dark cycle with free access to food and water. For therapeutic treatment, EAN rats receive i.p. injection of MS-275 (3.5 mg/kg) daily from day 10 to day 14 (six rats/group). For injection, MS-275 is suspended in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and the same volume (1 mL) of PBS is given to control rats. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 566.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 159-160ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C21H20N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 376.409 |
| Flash Point | 296.6±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 376.153534 |
| PSA | 106.34000 |
| LogP | 1.46 |
| Appearance | solid |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.672 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: 38 mg/mL, soluble |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P261-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29333990 |
|
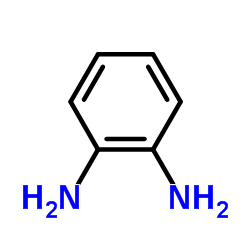
~82% 
209783-80-2 |
| Literature: WO2009/76206 A1, ; Page/Page column 16-17 ; WO 2009/076206 A1 |
|
~70% 
209783-80-2 |
| Literature: US6320078 B1, ; |
|
~89% 
209783-80-2 |
| Literature: ChemBioChem, , vol. 13, # 8 p. 1116 - 1120 |
|
~% 
209783-80-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 42, # 15 p. 3001 - 3003 |
|
~% 
209783-80-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 42, # 15 p. 3001 - 3003 |
|
~% 
209783-80-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 42, # 15 p. 3001 - 3003 |
|
~% 
209783-80-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 42, # 15 p. 3001 - 3003 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: ChemMedChem, , vol. 6, # 12 p. 2137 - 2141 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |