4373-41-5
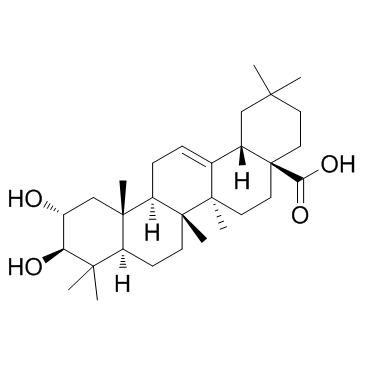
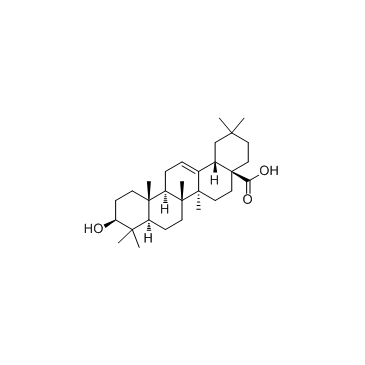
| Name | Maslinic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Maslinic acid
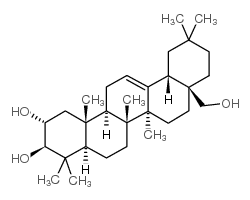
maslinicacid (2α,3β)- 2,3-dihydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid (4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10R,11R,12aR,14bS)-10,11-dihydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid Hawthorn Leaf Extract (2α,3β)-2,3-Dihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid Crataegolic acid (2α,3β)-2,3-dihydroxy-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid CRATEGOLIC ACID |
| Description | Maslinic acid can inhibit the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB p65 and abolish the phosphorylation of IκB-α, which is required for p65 activation |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p65 |
| In Vitro | Maslinic acid (MA) inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB translocation to nucleus and phosphorylation of IκB-α. Maslinic acid has also been reported to suppress NF-κB regulated osteoclastogenesis in bone marrow monocytes and inhibit TNF-α-induced NF-κB activity and its downstream genes’ expression in pancreatic cancer cells. To confirm if the anti-inflammatory effects of olive pomace extracts (OPEs) inRAW264.7 cells can be attributed to Maslinic acid, dose-dependence experiments determined the effective concentration of Maslinic acid to be 10-20 μM. 20 μM Maslinic acid significantly suppresses TNF-α production and inhibits IL-1, IL-6, and COX-2 mRNA expression in RAW 264.7 cell. Maslinic acid (at 10 and 20 μM) significantly suppresses the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB p65 in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Pretreatment with Maslinic acid significantly reduces the LPS-induced phosphorylation of IκB-α[1]. |
| In Vivo | Paw swelling is alleviated when mice are administered with 200 mg/kg Maslinic acid (MA), significantly suppressing inflammation, compared to the carrageenan induced control group, 4 h after λ-carrageenan injection (0.91±0.51 mm and 1.79±0.4 mm, respectively)[1]. |
| Cell Assay | RAW 264.7 cells are seeded in 96-well culture plates at a density of 1×105 cells/mL and after incubation for 24 h, are treated with OPE1 (300 μg/mL or 400 μg/mL), OPE2 (20 μg/mL or 40 μg/mL), or Maslinic acid (10 μM or 20 μM) , as well as with/without LPS at the same time. Cell viability i determined using the WST-1 reagent. Briefly, WST-1 reagent (10 μL) is added to each well and incubated for 1h in a humidified incubator. The absorbance of the samples measured at 450 nm (reference wavelength is 750 nm). Viability is expressed as a percentage of the absorbance measured in LPS-treated cells[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Five-week-old male Balb/c mice (19-21 g) are housed in a conventional condition and provided with the free access to standard rodent chow and water. Edema is induced by intraplantar injection of 100 μL 1% carrageenan into the hind left paw. Maslinic acid is tested initially at a dose of 200 mg/kg, orally administered 60 min before and after carrageenan injection. Paw thickness is measured using electronic digital calipers, 2, 3, and 4 h following carrageenan treatment. Mice are sacrificed by carbon dioxide inhalation 4 h after carrageenan injection[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 570.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 472.700 |
| Flash Point | 312.6±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 472.355255 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 7.87 |
| Appearance | white to off-white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.568 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | acetone: soluble1mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2940000000 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2940000000 |
|---|