Artemisitene
Modify Date: 2025-08-28 16:56:07
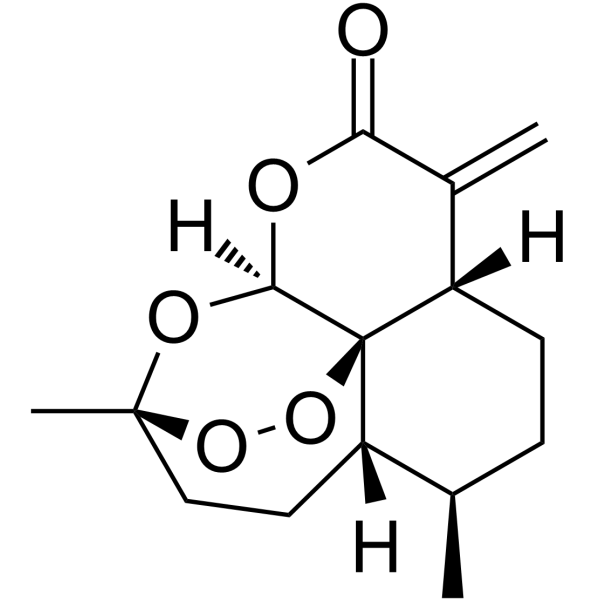
Artemisitene structure
|
Common Name | Artemisitene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 101020-89-7 | Molecular Weight | 280.32 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O5 | Melting Point | 160-162°C (lit.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of ArtemisiteneArtemisitene, a natural derivative of Artemisinin, is a Nrf2 activator with antioxidant and anticancer activities. Artemisitene activates Nrf2 by decreasing Nrf2 ubiquitination and increasing its stability[1][2]. |
| Name | Artemisitene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Artemisitene, a natural derivative of Artemisinin, is a Nrf2 activator with antioxidant and anticancer activities. Artemisitene activates Nrf2 by decreasing Nrf2 ubiquitination and increasing its stability[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Artemisitene selectively induces DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) and apoptosis in various human cancer cells by suppressing the expression of topoisomerases in human cancer cells. Artemisitene selectively destabilizes c-Myc in human cancer cells by promoting the ubiquitination of c-Myc through the specific induction of the c-Myc E3 ligase NEDD4[2]. |
| In Vivo | In Nrf2 wild-type mice, systemic administration of Artemisitene (5-10 mg/kg; i.p.) strongly inhibits bleomycin-induced lung damage[1]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 160-162°C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 280.32 |
| Exact Mass | 280.13100 |
| PSA | 53.99000 |
| LogP | 2.31500 |
| Vapour Pressure | 3.52E-07mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| artemisitene (methyl artemisinin) |