| Description |
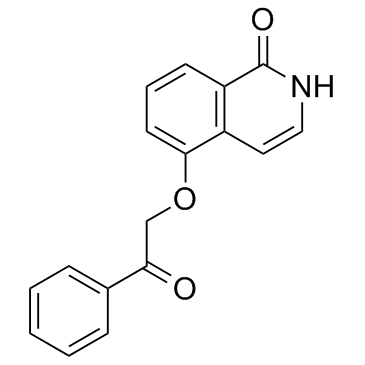
UPF 1069 is a PARP inhibitor, with IC50s of 8 and 0.3 μM for PARP-1 and PARP-2, respectively.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
PARP-2:0.3 μM (IC50)
PARP-1:8 μM (IC50)
|
| In Vitro |
UPF 1069 (Compound 55) is a PARP inhibitor, with IC50s of 8 and 0.3 μM for PARP-1 and PARP-2, respectively[1]. UPF 1069 (1 µM) reduces the residual PARP activity by approximately 80% of PARP-1-deficient fibroblasts, but only slightly inhibits the enzymic activity in wild-type fibroblasts. UPF 1069 (0.1-1 µM) markedly enhances CA1 hippocampal damage. UPF 1069 (10 µM) also exacerbates oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) damage in organotypic hippocampal slices. However, UPF 1069 alleviates the damage cuased by OGD in mixed cortical cell cultures, shows a potent neuroprotective activity both at a concentration (1 µM) selectively acting on PARP-2 and at a concentration (10 µM) inhibiting both PARP-1 and PARP-2 activities[2].
|
| Kinase Assay |
PARP activity is evaluated by utilizing commercially available recombinant bovine PARP-1 and mouse PARP-2. Briefly, the enzymatic reaction is carried out in 100 µL of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) containing 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM dithiothreitol, 10 µg sonicated calf thymus DNA, 0.2 µCi [adenine-2,8-3H]NAD and recombinant enzyme PARP-1 or PARP-2 (0.03 U per sample). Different concentrations of the putative inhibitors are added, and the mixture is incubated for 1 h at 37°C. The reaction is terminated by adding 1 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid (w/v) and centrifuged. Pellets are then washed twice with 1 mL of H2O and resuspended in 1 mL of 0.1 M NaOH. The radioactivity incorporated from [adenine-2,8-3H]NAD into proteins is evaluated by liquid scintillation spectrometry[2].
|
| References |
[1]. Pellicciari R, et al. On the way to selective PARP-2 inhibitors. Design, synthesis, and preliminary evaluation of a series of isoquinolinone derivatives. ChemMedChem. 2008 Jun;3(6):914-23. [2]. Moroni F, et al. Selective PARP-2 inhibitors increase apoptosis in hippocampal slices but protect cortical cells in models of post-ischaemic brain damage.
|